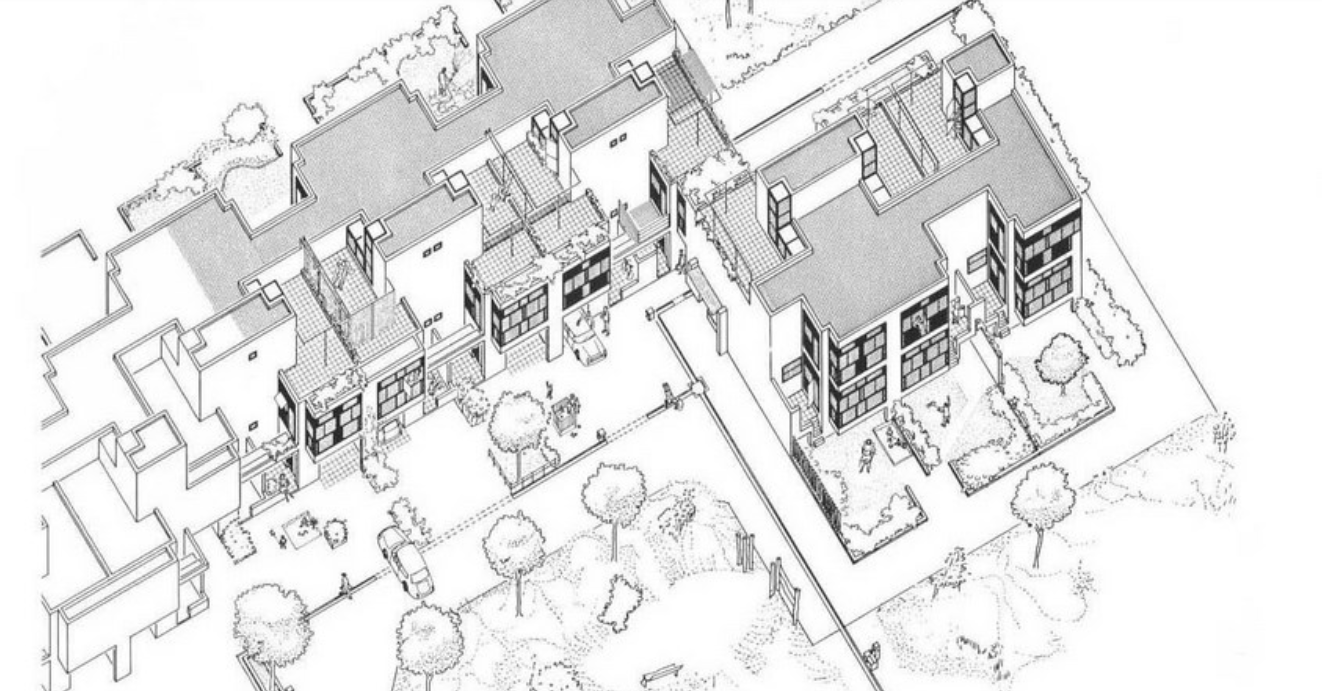
Diagoon Houses
Created on 11-11-2022
The act of housing
The development of a space-time relationship was a revolution during the Modern Movement. How to incorporate the time variable into architecture became a fundamental matter throughout the twentieth century and became the focus of the Team 10’s research and practice. Following this concern, Herman Hertzberger tried to adapt to the change and growth of architecture by incorporating spatial polyvalency in his projects. During the post-war period, and as response to the fast and homogeneous urbanization developed using mass production technologies, John Habraken published “The three R’s for Housing” (1966) and “Supports: an Alternative to Mass Housing” (1961). He supported the idea that a dwelling should be an act as opposed to a product, and that the architect’s role should be to deliver a system through which the users could accommodate their ways of living. This means allowing personal expression in the way of inhabiting the space within the limits created by the building system. To do this, Habraken proposed differentiating between 2 spheres of control: the support which would represent all the communal decisions about housing, and the infill that would represent the individual decisions. The Diagoon Houses, built between 1967 and 1971, follow this warped and weft idea, where the warp establishes the main order of the fabric in such a way that then contrasts with the weft, giving each other meaning and purpose.
A flexible housing approach
Opposed to the standardization of mass-produced housing based on stereotypical patterns of life which cannot accommodate heterogeneous groups to models in which the form follows the function and the possibility of change is not considered, Hertzberger’s initial argument was that the design of a house should not constrain the form that a user inhabits the space, but it should allow for a set of different possibilities throughout time in an optimal way. He believed that what matters in the form is its intrinsic capability and potential as a vehicle of significance, allowing the user to create its own interpretations of the space. On the same line of thought, during their talk “Signs of Occupancy” (1979) in London, Alison and Peter Smithson highlighted the importance of creating spaces that can accommodate a variety of uses, allowing the user to discover and occupy the places that would best suit their different activities, based on patterns of light, seasons and other environmental conditions. They argued that what should stand out from a dwelling should be the style of its inhabitants, as opposed to the style of the architect. User participation has become one of the biggest achievements of social architecture, it is an approach by which many universal norms can be left aside to introduce the diversity of individuals and the aspirations of a plural society.
The Diagoon Houses, also known as the experimental carcase houses, were delivered as incomplete dwellings, an unfinished framework in which the users could define the location of the living room, bedroom, study, play, relaxing, dining etc., and adjust or enlarge the house if the composition of the family changed over time. The aim was to replace the widely spread collective labels of living patterns and allow a personal interpretation of communal life instead. This concept of delivering an unfinished product and allowing the user to complete it as a way to approach affordability has been further developed in research and practice as for example in the Incremental Housing of Alejandro Aravena.
Construction characteristics
The Diagoon Houses consist of two intertwined volumes with two cores containing the staircase, toilet, kitchen and bathroom. The fact that the floors in each volume are separated only by half a storey creates a spatial articulation between the living units that allows for many optimal solutions. Hertzberger develops the support responding to the collective patterns of life, which are primary necessities to every human being. This enables the living units at each half floor to take on any function, given that the primary needs are covered by the main support. He demonstrates how the internal arrangements can be adapted to the inhabitants’ individual interpretations of the space by providing some potential distributions. Each living unit can incorporate an internal partition, leaving an interior balcony looking into the central living hall that runs the full height of the house, lighting up the space through a rooflight.
The construction system proposed by Herztberger is a combination of in-situ and mass-produced elements, maximising the use of prefabricated concrete blocks for the vertical elements to allow future modifications or additions. The Diagoon facades were designed as a framework that could easily incorporate different prefabricated infill panels that, previously selected to comply with the set regulations, would always result in a consistent façade composition. This allowance for variation at a minimal cost due to the use of prefabricated components and the design of open structures, sets the foundations of the mass customization paradigm.
User participation
While the internal interventions allow the users to covert the house to fit their individual needs, the external elements of the facade and garden could also be adapted, however in this case inhabitants must reach a mutual decision with the rest of the neighbours, reinforcing the dependency of people on one another and creating sense of community. The Diagoon Houses prove that true value of participation lies in the effects it creates in its participants. The same living spaces when seen from different eyes at different situations, resulted in unique arrangements and acquired different significance. User participation creates the emotional involvement of the inhabitant with the environment, the more the inhabitants adapt the space to their needs, the more they will be inclined to lavish care and value the things around them. In this case, the individual identity of each household lied in their unique way of interpreting a specific function, that depended on multiple factors as the place, time or circumstances. While some users felt that the house should be completed and subdivided to separate the living units, others thought that the visual connections between these spaces would reflect better their living patterns and playful arrangement between uses.
After inhabiting the house for several decades, the inhabitants of the Diagoon Houses were interviewed and all of them agreed that the house suggested the exploration of different distributions, experiencing it as “captivating, playful and challenging”1. There was general approval of the characteristic spatial and visual connection between the living units, although some users had placed internal partitions in order to achieve acoustic independence between rooms. One of the families that had been living there for more than 40 years indicated that they had made full use of the adaptability of space; the house had been subject to the changing needs of being a couple with two children, to present when the couple had already retired, and the children had left home. Another of the families that was interviewed had changed the stereotypical room naming based on functions (living room, office, dining room etc.) for floor levels (1-4), this could as well be considered a success from Hertzberger as it’s a way of liberating the space from permanent functions. Finally, there were divergent opinions with regards to the housing finishing, some thought that the house should be fitted-out, while others believed that it looked better if it was not conventionally perfect. This ability to integrate different possibilities has proven that Hertzberger’s experimental houses was a success, enhancing inclusivity and social cohesion. Despite fitting-out the inside of their homes, the exterior appearance has remained unchanged; neighbourly consideration and community identity have been realised in the design. The changes reflecting the individual identity do not disrupt the reading of the collective housing as a whole.
Spatial polivalency in contemporary housing
From a contemporary point of view, in which a housing project must be sustainable from an environmental, social and economic perspective, the strategies used for the Diagoon Houses could address some of the challenges of our time. A recent example of this would be the 85 social housing units in Cornellà by Peris+Toral Arquitectes, which exemplify how by designing polyvalent and non-hierarchical spaces and fixed wet areas, the support system has been able to accommodate different ways of appropriation by the users, embracing social sustainability and allowing future adaptations. As in Diagoon, in this new housing development the use of standardized, reusable, prefabricated elements have contributed to increasing the affordability and sustainability of the dwellings. Additionally, the use of wood as main material in the Cornellà dwellings has proved to have significant benefits for the building’s environmental impact. Nevertheless, while this matrix of equal room sizes, non-existing corridors and a centralised open kitchen has been acknowledged to avoid gender roles, some users have criticised the 13m² room size to be too restrictive for certain furniture distributions.
All in all, both the Diagoon houses and the Cornellà dwellings demonstrate that the meaning of architecture must be subject to how it contributes to improving the changing living conditions of society. Although different in terms of period, construction technologies and housing typology, these two residential buildings show strategies that allow for a reinterpretation of the domestic space, responding to the current needs of society.
C.Martín. ESR14
Read more
->

APROP | Temporary social housing for people at risk to residential exclusion
Created on 09-10-2024
Innovative aspects of the housing design/building
The APROP design and construction system is based on prefabricated modules, providing dignified and energy efficient dwellings for members of society who have difficulties in accessing housing. The homes achieve an AA Energy Rating, which the Barcelona municipality equates to a level of energy consumption four to six times lower than that of a conventional building of the same characteristics (Ajuntament de Barcelona, 2019a). Circularity is integral to the concept of the project, with upcycled shipping containers forming the structure, which would otherwise be considered as waste and sent to landfill. In terms of time and cost savings, owing to the dry and lightweight structure the entire building can be disassembled in four weeks are reassembled elsewhere, significantly reducing on-site construction time.
APROP has been documented as an exemplary project by the municipality and features in the “Innovation in affordable housing Barcelona” and “Barcelona right to housing” reports (Ajuntament de Barcelona, 2018; Hernández Falagán, 2019). The architectural team includes three practices: Straddle3 and Eulia Arkitektura in the design stage, and Yaiza Terré for the delivery stage. Following the announcement of the Bauhaus award, a prize that aims to demonstrate sustainability in alignment with the European Green Deal (European Commission, 2022), Housing Europe declared APROP “an emerging housing model” (Housing Europe, 2021). The project has also been recognised by various other local and international awards (Ajuntament de Barcelona, 2022). Although APROP is built to the same building standards as conventional housing in Barcelona, it received a critical response from a UK newspaper article (The Guardian, 2019), which raised concerns over the danger of lowering standards in the quality of housing if replicated elsewhere. Re-purposing shipping containers to provide housing has become an established industry in many countries but can typically lead to poor thermal and acoustic performance if it is not done well. This was highlighted in the same article by the principal architect David Juárez from Straddle3, who asserted that "building with containers can bring terrible results unless you really make an effort".
Methodology and research project by ATRI
The APROP programme is the result of research carried out by Tactical Accommodations of Inclusive Repopulation (ATRI), an interdisciplinary team supported by the Barcelona municipality that consists of architects, builders, economists, a lawyer, and a social scientist. The group was initiated in response to a lack of social and emergency housing in the Barcelona region. The project framework was formed between the Department of Social Rights, Cooperativa Lacol (the architects responsible for housing cooperative “La Borda”), Bestraten Hormias Arquitectura, and architectural practice Straddle3. ATRI cite the thesis project of architectural scholar Gerardo Wadel on Industrialised Construction and sustainability as further theoretical grounding for the APROP programme (ATRI, n.d.-a; Wadel, 2009). The methodology crosses disciplines to encompass four key areas: urbanism, architecture, economy, and management. This research culminated into the three main characteristics of an ATRI building: reversibility, being lightweight, and minimising execution time.
Construction characteristics, materials and processes
The prefabricated construction method and modular design strategy are characteristic of Industrialised Construction. Although the project is based on off-site construction, this did not take place in a factory setting and traditional manual labour was used (Ajuntament de Barcelona, 2019b). The prefabricated modules were transported through the narrow inner-city streets and placed on site within a steel frame using a large tonnage crane. The lightweight corrugated steel containers used were “last trip” containers that are easily available in the coastal port city of Barcelona, meaning the amount of embodied carbon to transport the containers was more minimal compared to further inland locations. Shipping containers are based on international ISO standards and are designed to universal sizes and can support their own weight whilst being stackable. Therefore, making changes to the structure to provide openings for doors and windows compromises their structural integrity and requires additional structural support. Considering the need to scale up production of the programme and the need to modify the structure, the construction system could potentially be modified in the future to use steel beams and columns formed from recycled material, rather than reusing steel in the form of shipping containers.
The apartments integrate underfloor heating to provide efficient thermal comfort for residents, whilst the double skin façade ensures the homes do not overheat. The skin includes a translucent outer layer made from cellular polycarbonate and timber to increase natural daylight. This also serves to visually adapt the building to its context and allows the shipping containers beneath to be visible. Knauf products were used to create a double plate system in the ceilings and partitions for a structural 60-minute fire rating. The modules, façade and roof incorporate dismountable dry joints for disassembly, recycling, and to enable the easy relocation of parts or whole buildings if necessary.
Energy performance characteristics
The project team claim APROP housing reduces energy consumption by 25% and greenhouse gas emissions by 54% (European Commission, 2021). The double skin façade, layout, and the use of photovoltaics significantly contributed to the achievement of the AA energy certification. These design decisions were tested during the design process using energy simulation models and collaboration with an energy and resource efficiency consultancy (European Commission, 2021). Energy is supplied by an aerothermal heat pump that extracts energy from the ambient air, which is more energy efficient compared to conventional methods. Passive design strategies are also incorporated with exterior openings positioned to produce cross ventilation and maximise sunlight during the winter and shade in the summer months. These techniques significantly reduce heating and cooling demands and further improve the energy efficiency performance.
Financial benefits
The APROP Gothic pilot project cost €940,000. The reuse of shipping containers is reported to have resulted in a 10% material reduction in construction costs compared to traditional methods, in addition to cost savings from a much shorter project programme. These savings are referred to as the Pre-Manufactured Value (PMV) in relation to Industrialised Construction methods, as outlined in the Farmer report (Farmer & Thornton, 2021). The APROP system offers the possibility of further cost savings if the project is replicated through economies of scale; plans are already underway for multiple APROP projects in the city to provide permanent social housing in additional to temporary housing. Work on the second pilot project, a block of 42 dwellings in El Parc i la Llacuna del Poblenou, began in January 2022.
A.Davis. ESR1
Read more
->

Solar Decathlon Europe 2022
Created on 21-11-2024
Relationship to urban environment
The SDE 2022 competition called for innovative urban housing solutions within existing contexts, allowing teams to choose from one of three scenarios: (1) a vertical extension adding additional storeys, (2) closing gaps between buildings, or (3) a horizontal extension. Among the sixteen built projects, eleven were top-ups, four were in-fill, and one was a horizontal extension. Some teams opted for a top-up solution for the existing Café Ada site in Wuppertal, whilst others produced solutions tailored to a local context of their home country. Despite the diverse origins of the projects, all of them had to be transported and operated at the Solar Campus in Wuppertal, Germany. Table 1 shows the results of the competition, which was won by team RoofKIT from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology. Note that the third place was tied between teams SUM from TU Delft and Aura from Grenoble School or Architecture.
Innovative aspects of the housing design/building
As documented in the competition Source Book (Voss & Simon, 2022), the teams developed various innovative biological, low-carbon, and circular materials and products from various other sectors, such as mycelium bound insulation, sea grass, recycled newspapers, jeans for insulation, and recycled yoghurt pots for kitchen and bathroom joinery. Chalmers University’s Team Sweden experimented with 3D printed cellulose whilst team X4S from Biberach University of Applied Sciences used tubular thin film photovoltaics, originally developed for large-scale use in agriculture, as pergola roofing. Innovative layouts included tessellating modules to provide multiple configurations, and highly efficient living units for multiple households (SDE, 2022).
Construction characteristics, materials and processes
All teams used Industrialised Construction (also known as Modern Methods of Construction in the UK) to varying degrees to prefabricate their buildings in their home countries. Construction included timber-based 3D modular and 2D panelised elements, and the competition also required the use of BIM to model the designs. To be able to disassemble and reassemble the HDUs they had to avoid the use of glues and wet sealants and instead join the building parts using various forms of reversible connections. Strategies included interlocking wood jointing, steel plates and footings, tapes, and mechanical joints such as screws, rivets, and bolts (Voss & Simon, 2022). These joining methods were designed to withstand water-ingress as well as airtightness, which was tested using the blower door test.
Energy performance characteristics
High energy efficiency performance and the production of on-site renewable energy were critical design aspects of the competition. All homes were designed to use electricity as the sole energy source for energy services and were powered by air- and ground-source heat pumps, and photovoltaic panels were integrated both horizontally on roofs and vertically on façades, depending on whether the project responded as an infill or top-up solution (Voss & Simon, 2022). Nine HDUs met the Passive House standard and included innovative passive strategies, such as solar chimneys, which were implemented by five teams, including Azalea from the Polytechnic University of València. Eight of the sixteen teams were chosen to remain on-site for an additional 3-5 years after the competition as Living Labs to provide in-use research data (University of Wuppertal, 2022).
Involvement of other stakeholders
The competition incorporates a level of entrepreneurship, with teams encouraged to forge partnerships and gain sponsorship from various industry partners. This provided teams with a mixture of financial support, in-kind services, or donations of materials and products. The extent of collaboration with partners and sponsors varied across the teams: these were formed not only with contractors and product suppliers, but in some cases with housing associations and local municipalities as well. The involvement of stakeholders from different fields not only fostered collaboration between fields, but brought about innovative construction solutions, bridging the gap between academia and industry.
A.Davis. ESR1
Read more
->
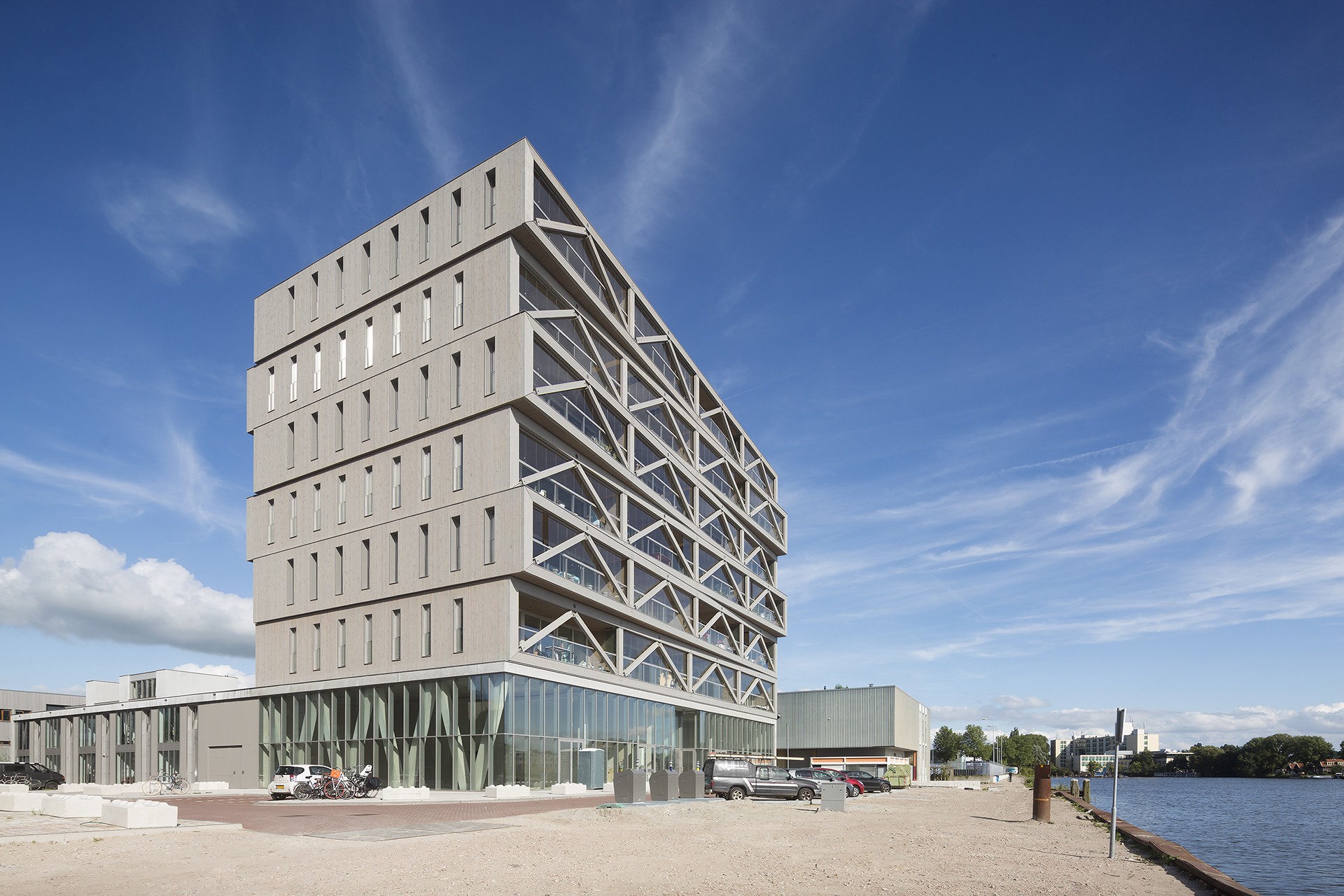

Patch22
Created on 05-12-2023
A response to environmental and economic challenges
The initiators of Patch22, architect Tom Frantzen and building manager Claus Oussoren, aimed at achieving together what they couldn’t manage in previous commissions independently: an oversized wooden structure characterised by flexibility, distinctive architecture, and a strong commitment to sustainability. They established the development company Lemniskade Projects to pursue their goals (Frantzen et al architecten, 2017). Winning the Amsterdam Buiksloterham Sustainability tender in 2009, Patch22 was not only recognised for its exceptional sustainability scores but also for its innovative circular design approach and its capability to adapt to unforeseen future uses. The project's primary objectives were rooted in environmental sustainability, employing renewable and reusable materials, particularly wood for the main structure and facade. Embracing Open Building principles, Patch22 sought maximum flexibility in dwelling sizes and layouts, offering an ingenious response to the environmental and economic challenges outlined in the tender (Kendall, 2021). The 30-meter-tall wooden structure currently hosts 33 dwellings with diverse sizes ranging from 40 m² to 204 m². The building promotes long-term adaptability, as it is prepared to be easily subdivided into six independent office floors or a maximum of 48 apartments (Frantzen, 2023). This showcases how a single support structure can serve multiple generations, accommodating the dynamic needs of its users while addressing some of the current environmental challenges such as material waste, the construction industry’s carbon footprint or the implementation of design for disassembly practices.
A flexible and adaptable building
A flexibility of a building can be enhanced when traditional architectural elements are reassessed. Various strategies were employed to maximize the adaptability of use, layout design, and apartment sizes:
No load-bearing division walls
The timber laminated post and beam structure, in combination with lightweight division walls, became crucial to ensure size variations between apartments and a greater freedom of choice in defining the layouts. Additionally, by superimposing the residential and office regulations, introducing a generous floor height of 4 m, and structurally supporting floor loads of 4 KN, the building accommodates the potential for entirely or partially utilising residential spaces for office purposes (Frantzen et al architecten, 2017).
No vertical shafts inside the apartment
In conventional housing, meter cabinets, kitchens, and bathrooms have typically been constructed near vertical shafts to minimise the length of the drains. When developing Patch22, it was unknown which units would merge to form a single apartment, making it challenging to position the vertical shafts. Two shafts were integrated into the structural core, with pre-installed drains, water and electricity conduits running up to each front door, from where they could be extended to the desired location in an apartment (Council on Open Building, 2023).
Hollow floors to run services horizontally
Patch22 adopts a horizontal services distribution, a common practice in office buildings. The necessary inclination of a toilet drain from the central shaft to the outermost corner of the building results in a floor build-up increase to 50cm. This available space for conduits enables the placement of kitchens and bathrooms anywhere within the dwelling. This departure from the traditional clustering of humid spaces in residential buildings facilitates the creation of multiple floor layouts that respond to the users’ needs.
No meters inside the apartment
By relocating the heavily regulated meters and main switches to the ground floor and placing the non-regulated secondary fuse boxes at each level, Patch22 provides open spaces which can be subdivided in multiple ways (Frantzen, 2023). The independence of the meters from the dwellings streamlines future adaptations with minimal disruptions to the individual living spaces.
Smaller subdivision of legal entities
From a technical perspective, designing a flexible and adaptable building is feasible. But it is also necessary to provide the legal mechanisms that make it possible. In the case of Patch22, each floor contains 8 legal units that can be combined horizontally or vertically (Frantzen, 2023). Although, in its current state, most floors have 3-6 dwellings per flight, these legal units could be divided or merged, sold, or rented independently, used as office or as residential spaces.
Designing for the unknown
Embracing the philosophy advocated by Habraken (OpenBuilding.co, 2023), Patch22 prioritises designing for the unknown. Strategies include over-dimensioning the structure, simultaneous compliance with diverse regulations for different uses, incorporating extra entrance doors, and providing space for additional mailboxes. These approaches keep the design open for future changes, ensuring long-term adaptability.
A sustainable proposal
Patch22 embodies sustainability across multiple dimensions. Environmentally, the building achieves sustainability through a series of strategies: improving energy efficiency, using renewable materials, and fostering layout flexibility. The 2009 design garnered a GPR score of 8.9 and an EPC of 0.2, showcasing its commitment to sustainable practices. The roof, covered with photovoltaic panels, makes the building energy-neutral, while the rainwater collection feeds into a grey water system. The adoption of CO2-neutral pellet stoves, utilising compressed waste wood as fuel, further underlines Patch22’s commitment to eco-friendly energy sources (Frantzen et al architecten, 2017). Despite the challenges posed by fire and acoustic regulations, the building boldly features wood as its main material, with additional thickness added to columns and beams to comply with safety standards. This decision, although increasing costs, remains more economical than the alternative solution of building with 2D CLT panels (Frantzen, 2023). Additionally, the emphasis on long-term layout flexibility aligns with environmental sustainability by reducing waste during future adaptations and facilitating component disassembly. From a social standpoint, involving residents in the design process fostered diversity and strengthened the sense of belonging. Finally, the economic sustainability of Patch22 is evident in its adaptable support, serving as a long-term investment that evolves with changing needs, potentially acquiring different uses over time, benefitting both the planet and the economic interests of its users.
Construction characteristics
The support components, encompassing the structure, façade, and core of Patch22, are highly prefabricated, facilitating a swift and precise assembly process on-site while minimising waste and reducing disruptions. The structure incorporates over-dimensioned laminated wooden beams and columns, along with vertical core constructed with prefabricated concrete panels (Open Building NOW!, 2020). The NW and SE façades employ CLT panels with a thickness of 220mm, while the NE and SW orientations, serving as the main facades, create loggias on both sides. The loggia's interior façade features modulated sliding doors with CLT prefabricated frames, allowing for the free placement of interior partitions by strategically positioning mullions every 3 meters (Frantzen, 2023). Externally, the loggia is characterised by redwood truss beams with bolted connections to steel joints which facilitate their future disassembly. These buffer zones can be fully enclosed with glazed modular panels in winter or left open with a fixed handrail during the summer.
The floor plays a pivotal role in leveraging the flexibility of the apartments within the structure. Employing a Slimline structural flooring system made of IPE 400 steel profiles and a 70mm reinforced concrete slab below, this design allows services to run efficiently within the hollow floor, reaching even the most remote corners of each apartment. After installing drains and other facilities, the floor is topped with an acoustic membrane, a Lewis profile sheet, and 8cm of anhydrite screed with underfloor heating. While initially considering demountable top floor tiles, this solution was deemed complex and expensive compared to the anhydrite screed, which proved more cost-effective and flexible (Frantzen, 2023). By planning in advance for the placement of maintenance registration points to the floor cavity, it was possible to enable access for the necessary alterations while maintaining practicality and affordability.
User customisation process
The customisation process at Patch22 began with a search for prospective residents through social media, leveraging it as a platform to connect with individuals interested in actively designing their living spaces in collaboration. Once on board, residents were presented with the opportunity to shape their homes within an entirely empty interior. A catalogue of multiple variations was offered by the architects, allowing some residents to select a pre-designed option that suited their preferences. Alternatively, others opted for a more collaborative approach, working closely with Frantzen architects to create a custom layout. Some residents took an independent venue, either designing their dwellings themselves or hiring another architect to develop their interiors (Frantzen, 2023). Throughout the process, Frantzen provided comprehensive guidance on the technical requirements, ensuring compliance with fire and soundproofing regulations. Residents could choose to have the base installations in the floor installed by the main contractor or to receive the bare shell and install them themselves. This inclusive approach allowed residents to actively contribute to the unique character of Patch22 while ensuring the resiliency of the building support for future generations.
C.Martín. ESR14
Read more
->

Flexwoningen Oosterdreef
Created on 09-02-2024
Background
The soaring housing shortage in the Netherlands has prompted national and local governments to come up with innovative solutions to cater for the ever-increasing demand. The Flexwonen model is a response to the need to provide homes quickly and to foster circularity and innovation in the construction sector. The model is crafted to meet the housing needs of people who cannot simply wait for the lengthy process of conventional housing developments or cannot afford to remain on the endless waiting list to be allocated a home.
Flexibility is its main characteristic. This is reflected not only in the design and construction features of the housing buildings, but also in the regulatory frameworks that make them possible. The faster the units are built and delivered, the greater the impact on people’s lives. This dynamic approach, which adapts to existing and evolving circumstances of homebuilding, relies on collaboration between stakeholders in the sector to streamline the procurement and building process. All of this is accompanied by an integrated approach to placemaking, exemplified by the partnership with a local social organisation, the involvement of a community builder, the provision of spaces for residents to interact and get to know each other, the project's target groups and the beneficiary selection process.
Flexwonen can have a significant impact on municipalities and regions that are severely affected by housing shortages, especially those lacking sufficient land and time to develop traditional housing projects. Due to its temporary nature, homes can be built on land that is not suitable for permanent housing. This streamlines the building process and allows the development of areas that are not currently suitable for housing, both in urban and peri-urban zones. After the initial site permit expires, the homes can be moved to another site and permanently placed there.
Recent developments in construction techniques and materials contribute to raising the aesthetic and quality standards of these projects to a level equivalent to that of permanent housing, as the case of Oosterdreef in Nieuw-Vennep demonstrates. Nevertheless, this model, propelled by the government in 2019 with the publication of the guide ‘Get started with flex-housing!’ and the ‘Temporary Housing Acceleration taskforce’ in 2022 (Druta & Fatemidokhtcharook, 2023), is still at an embryonic stage of development. The success of the initiative and its real impact, especially in the long term, remain to be seen.
Analogous housing projects have been carried out in other European countries, such as Germany, Italy, and France among others (See references section). Although their objectives and innovative aspects resonate with the ones of Flexwonen in the Netherlands, the nationwide scope of this model, sustained by the commitment and collaboration between national and local governments, social housing providers and contractors, is taking the effects of policy, building and design innovation to another level.
Involvement of stakeholders
The national government's aim to establish a more dynamic housing supply system, capable of adapting to local, regional or national demand trends in the short-term, has prompted municipalities like Haarlemmermeer to join forces with housing corporations. Together, they venture into the production of housing that can leverage site constraints while contributing to bridging the gap between supply and demand in the region.
Thanks to its innovative, flexible and collaborative nature, the Oosterdreef project was completed in less than a year after the first module was placed on the site. The land, which is owned by the municipality, is subject to environmental restrictions due to the noise pollution caused by its proximity to Schiphol airport, meaning that the construction of permanent housing was not feasible in the short term. Nevertheless, the pressing challenge of providing housing, especially for young people in the region, priced out by the private market, has led the municipality to collaborate with a housing corporation and an architecture firm. Together, they have developed a ‘Kavelpaspoort’ (plot passport), a document that significantly expedites the building process.
The plot passport is a comprehensive framework that summarises a series of requirements, restrictions, guidelines and details in a single document, developed in consultation with the various stakeholders involved. Its main purpose is to expedite the construction process. Its various benefits include helping to shorten the time it takes for the project to be approved by the relevant authorities, facilitating the selection of a suitable developer and contractors, and avoiding unforeseen issues during construction. The document is also an effective means of incorporating the voices of relevant stakeholders, including local residents before any work begins on the site. This ensures transparency and participatory decision-making. In Oosterdreef, Ymere, the housing corporation that manages the units, and FARO, the architecture firm commissioned with the design, played pivotal roles in drafting the document in collaboration with the municipality of Haarlemmermeer. Their main objective was to swiftly build houses using innovative construction techniques and to provide much-needed housing on a site that was underused due to land restrictions.
Project’s target groups and selection process
Perhaps one of the most compelling aspects of the model is the diverse group of people it intends to benefit. The target groups of Flexwonen vary according to context and needs, as the municipalities are in charge of establishing their priorities. In the case of Oosterdreef, Ymere and Haarlemmermeer aim for a social mix that not only contributes to solving the housing shortage in the region, but also supports the integration process of the status holders. The selection of status holders, i.e. asylum seekers who have received a residence permit and therefore cannot continue living in the reception centres, who would benefit from the scheme, was carried out in collaboration with the municipality and the housing corporation. As most of these residents did not previously live in the local area, as the central government determines the number of status holders that each municipality must accommodate, the social mix is attained by also including local residents. In this case, they were allocated a flat in the project based on a specific profile, as the flats were designed for single people. The project, which comprises 60 dwellings, is therefore deliberately divided to accommodate 30 of the above-mentioned status holders and 30 locals.
In addition, the group of locals was completed with emergency seekers (‘Spoed- zoekers’) and starters. The emphasis that the project's focus on this population swathe emphasises its social function. Emergency seekers are people who are unable to continue living in their homes due to severe hardship, including circumstances that severely affect their physical or mental well-being, and who are otherwise likely to be at risk of homelessness. This includes, for example, victims of domestic violence and eviction, but also people going through a life-changing situation such as divorce. On the other hand, starters, in this project between the ages of 23 and 28, refer to people who long to start on the housing ladder, e.g., recent graduates, young professionals, migrant workers and people who are unable to move from their parental home to independent living due to financial constraints.
Finally, local residents interested in the project were asked to submit a letter of motivation explaining how they would contribute to making Oosterdreef a thriving community, in addition to the usual documentation required as part of the process. Thus, a stated willingness to participate in the project was deemed more important than, for example, a place on the waiting list, demonstrating the commitment of the housing corporation and local authorities to creating a community and placemaking.
Innovative aspects of the housing design
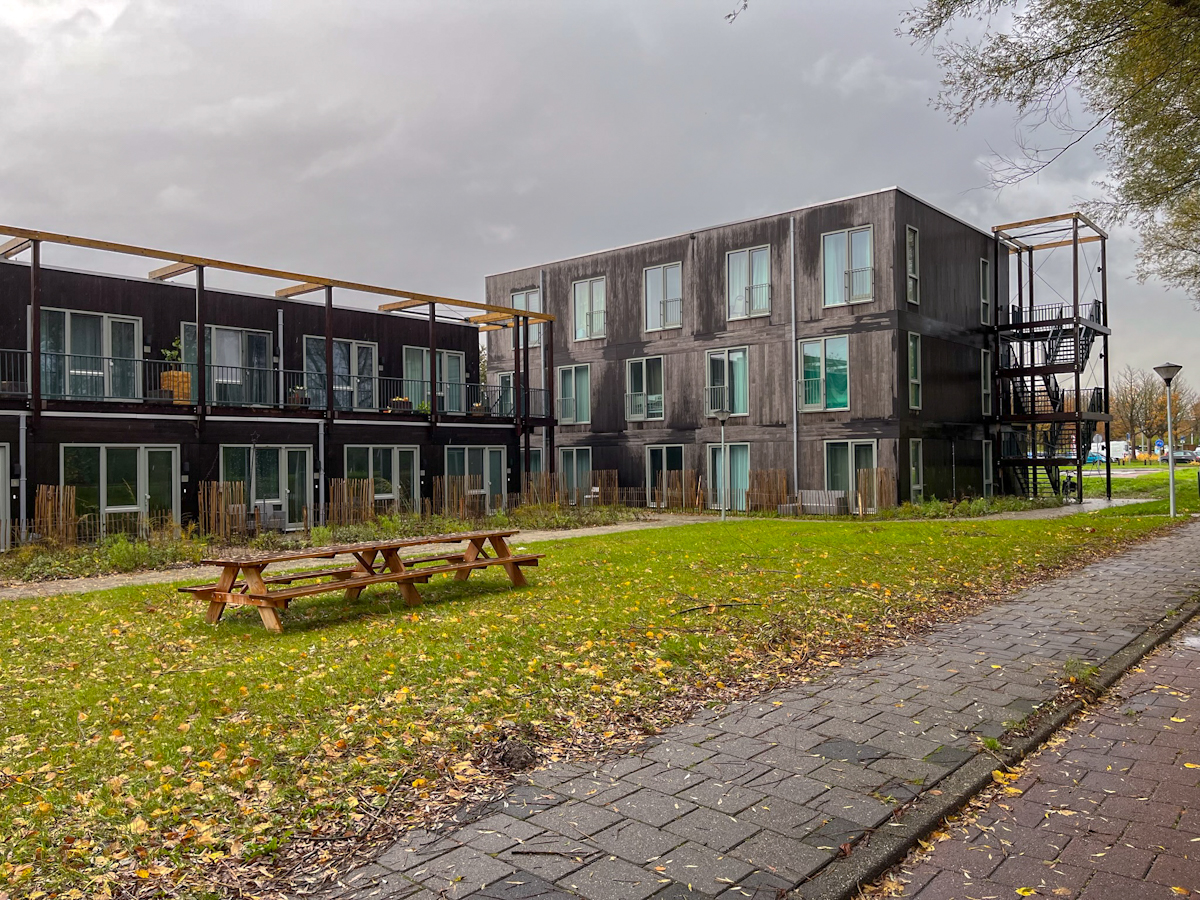
Although this model has been applied to a range of buildings and contexts, from the temporary use of office space to the retrofitting of vacant residential buildings and the use of containers in its early stages of development (which has had a significant bearing on the stigmatisation of the model), one of the most notable features of the government's current approach to scaling up and accelerating the model is its support for the development of innovative construction techniques. The use of factory-built production methods such as prefabricated construction in the form of modules that are later transported to the site to be assembled could help to establish the model as a fully-fledged segment of the housing sector. An example of this is Homes Factory, a 3D module factory based in Breda, which was chosen as the contractor. Prefab construction not only significantly reduces the construction phases, but also makes it easier to relocate the houses when the licence expires after 15 years, which contributes to its flexibility.
The architecture firm FARO played a crucial role in shaping the plot passport, which incorporated details on the design and layout of the scheme. The objective was to encourage social interaction through shared indoor and outdoor spaces, organized around two courtyards. These courtyards are partially enclosed by two- and three-storey blocks, featuring deck access with wider-than-usual galleries with benches that offer additional space for the inhabitants to linger. Additionally, facilities such as letterboxes, entrance areas, waste collection points, and covered bicycle parking spaces were strategically placed to foster spontaneous encounters between neighbours. Some spaces, such as the courtyards, were intentionally left unfinished to encourage and enable residents to determine the function that best suits them. This provides an opportunity for residents to get to know each other, integrate, and cultivate a sense of belonging.
Within the blocks, the prefab modules consist of two different housing typologies of 32 m2 and 37 m2. One of these units on the ground floor was left unoccupied to be used as a common indoor space. The ‘Huiskamer’ or living room according to its English translation, is strategically located at the heart of the scheme, adjacent to the mailboxes and bicycle parking space. Besides serving as a place for everyone to meet and hold events, it is the place where a community builder interacts and works with the residents on-site.
Construction and energy performance characteristics
The environmental sustainability of the building was at the top of the project's priorities. Off-site construction methods offer several advantages over traditional techniques, including reduced waste due to precise manufacturing at the factory, efficient material transport, less on-site disruption, shorter construction times and the reusability and circularity of the materials and the units themselves. The choice of bamboo for the façades also contributes to the project's sustainability. Bamboo is a highly renewable and fast-growing material compared to traditional timber, with a low carbon footprint as it absorbs CO2 during growth (linked to embodied carbon). It also has energy-efficient properties, such as good thermal regulation, which leads to lower energy consumption (operational carbon). This is complemented by a heat pump system and solar panels on the roofs of the buildings.
“The only thing that is not permanent is the site”
This sentiment was shared by many, if not all, individuals involved in the project whom I had the opportunity to interview for this case study. The design qualities of the project meet the standards expected for permanent housing. One of the main challenges faced by projects of this type is the perception, increasingly erroneous, that their temporary nature implies lower quality compared to permanent housing.
In this case, the houses were designed and conceived as permanent dwellings, the temporary aspect is only linked to the site. When the 15-year licence expires, the homes will be relocated to another location where they can potentially become permanent. They can also be reassembled in a different configuration if required, a possibility granted by the modular design of the dwellings.
Integration with the community
The residents were selected with the expectation that they would contribute to building a community and support the permit-holders to better adapt and integrate into the local community and surroundings. Ymere, together with a local social organisation, helps new residents in this process of integration. During the first two years following the completion of the construction phase, concurrent with tenants moving into their new homes, an on-site community builder works with residents to help them forge the social ties that will enable the development of a cohesive and thriving community. The community builder has organised a range of social activities and initiatives in collaboration with the residents in the shared spaces. These include piano lessons, communal meals, sporting activities and ‘de Weggeefkast’, or the giveaway cupboard, a communal pantry aimed at fostering a sense of neighbourly sharing and cooperation.
L.Ricaurte. ESR15
Read more
->

WikiHouse: South Yorkshire Housing Association
Created on 16-10-2024
South Yorkshire Housing Association manages 6,000 homes to provide social and affordable rent housing for over 10,000 residents (SYHA, n.d.). The housing association is helping to lead the way in less conventional construction methods, utilising industrialised construction to deliver a portion of its homes. As a founding member of the Off Site Homes Alliance (OSHA, n.d.), SYHA is also part a framework and network of registered housing providers, local authorities, contractors, and strategic partners, dedicated to delivering high-quality, affordable housing produced using both 2D panelised and 3D volumetric approaches.
The two semi-detached WikiHouses, with an approximate floor area of 70m², are situated in Sheffield, close to the city centre. They were delivered in collaboration with product design providers Open Systems Lab, architects Architecture 00, engineers Momentum, manufacturers Chop Shop, and assembly and installation were carried out by Castle Building Services supported by Mascot Management. The project is not only exemplary in reducing embodied energy in housing but also proves to be energy efficient, having earned runner-up in the Ashden Awards for Energy Innovation.
Design
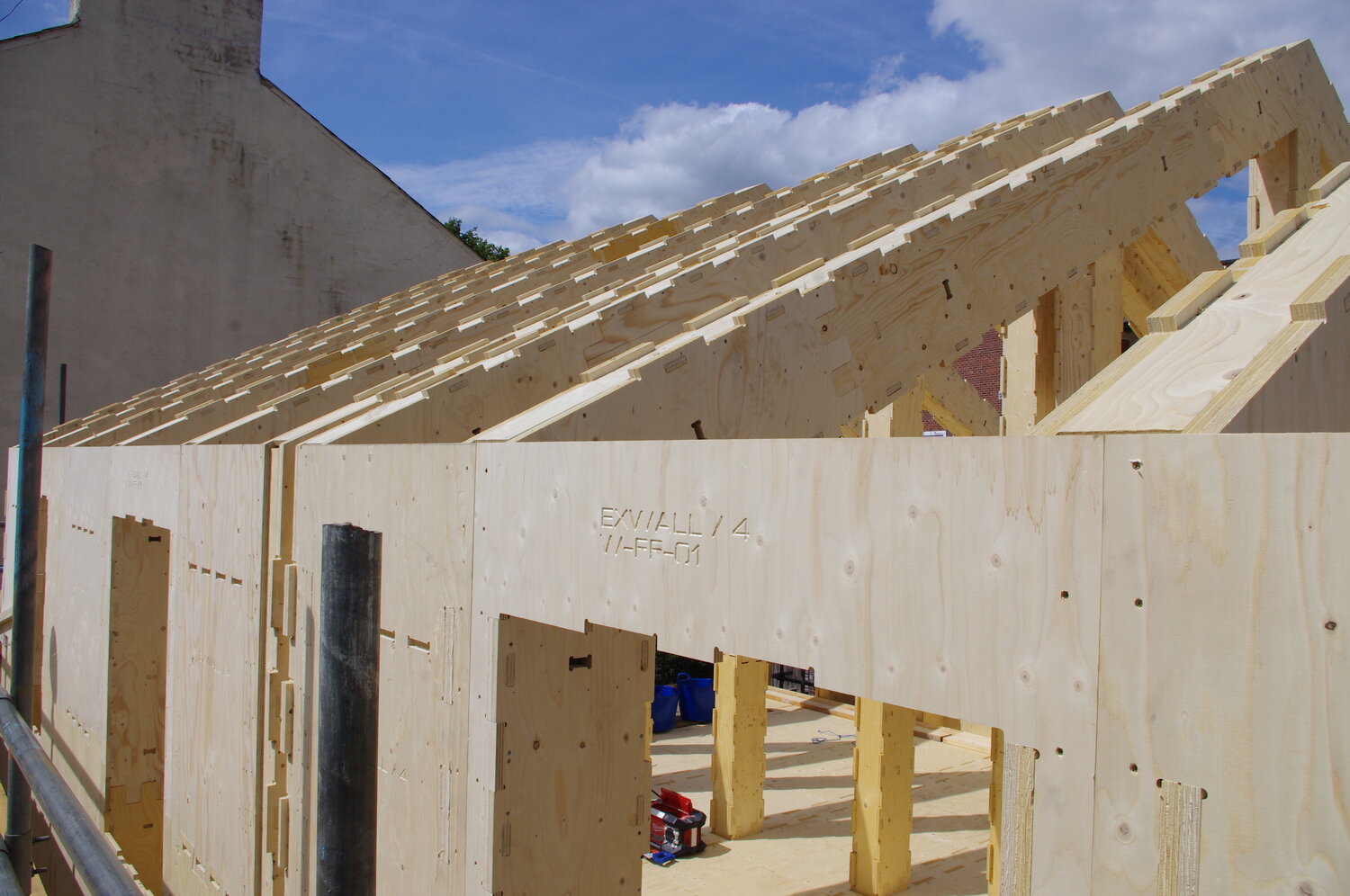
WikiHouse aims to democratise housing with the creation of standardised and open-source designs incorporating industrialised construction, based on foundational principles such interoperability and a lean approach inspired by the Toyota Production System (WikiHouse, n.d.-a). WikiHouse provided SYHA with a “jigsaw of pieces” in the form of panelised components designed to be assembled around a framing system. The system was made from simple plywood construction, with no need for steel due to the proposed low building height. Timber is not only ideal for buildability and deconstruct-ability as a lightweight material, but it also possesses carbon sequestering properties. It should be noted the open-source product can be limiting for some adopters of WikiHouse as additional design, construction and installation services are not included. SYHA therefore needed to fill the gap between the product and delivery to their end-users.
Manufacturing
WikiHouse products lend themselves to self-build construction or utilisation of ‘micro’ factories. SYHA’s pilot used localised construction to manufacture the plywood frame using digital files, cut by CNC machining company ‘Chop Shop’, located just 1 mile from the site (Plowden, 2020). Cutting the pieces was a fast and efficient process, which was designed to minimise material waste. Chop Shop also assisted by storing the building parts until the site was ready for assembly due to the lack of on-site storage space. WikiHouse seems to be well suited to manufacture by a distributed network of small manufacturers. However, according to SYHA, there is potential for scalability with larger housing association schemes in future. In addition, the production strategy is ideal to unlock small, tricky sites within the housing association’s portfolio, facilitating the production of high-quality housing with high circularity potential.
Transport and assembly
The dimensions of the timber frames were small enough to be delivered to site using a transit van rather than a larger lorry, which proved to be more manageable and cost effective. Once on site, the prefabricated building parts were assembled “like a jigsaw” using a step-by-step manual, although SYHA felt the instructions could be enhanced in the future to improve delivery by a range of stakeholders (Plowden, 2020).
The project programme was much shorter compared to a traditional build, the first home was manufactured and assembled in under a month. This process was even faster for the second home due to the experience gained from the first home, highlighting potential to improve efficiency for larger schemes in the future. As prefabrication and assembly are still unconventional, the transition between these processes may present additional complexity for the stakeholders involved compared to a traditional build.
In the case of SYHA’s WikiHouse, Miranda found “the manufacturer saw its job as providing the cut pieces for the installer to install, they didn't appreciate that they were part of a manufacturing process with the installer”. She went on to highlight that manufacturers and installers are typically separate parties in the UK, with installers often being main contractors who aren’t used to off-site methods. The team also had to overcome issues with unexpected ground conditions which hadn’t been included within the original site survey, though this was unrelated to the construction system used.
Building performance
SYHA’s WikiHouse homes have so far proven to be warm and energy efficient, resulting in low energy bills for residents, owing to the high-level of insulation within the plywood structure and panelling. The building strategy ensures easy maintenance and access during the use phase without disturbing residents. This was achieved by incorporating exterior services coupled with dry construction techniques. As a result of their involvement in the whole process, SYHA is able to effectively manage disassembly for future maintenance and potential adaptations, as their Home Maintenance Team were able to observe how the WikiHouses were assembled.
Legal
Providing the design and detailing are correctly implemented, meeting UK building regulations is not an issue with the WikiHouse system, which claims its products will exceed the requirements of UK building regulations (WikiHouse, n.d.-b). However, it proved more difficult to obtain the building warranty for the SYHA pilot. All new products need to be warranted, which requires warranters to inspect the whole building process to guarantee the necessary requirements are met.
SYHA’s WikiHouse utilised the Buildoffsite Property Assurance Scheme (BOPAS) (n.d.), which is a specialist warranty provider for buildings using industrialised construction, referred to as Modern Method of Construction (MMC) in the UK. Homes with BOPAS accreditation are readily mortgageable for a minimum of 60 years.
Financial
Using an off-site approach can be financially advantageous, as more time is invested upfront to plan, design, and manufacture. This shortens the time spent on-site and therefore reduces preliminary costs for the operation of the construction site. Although the project benefitted from a shortened timeline due to the industrialised approach, the WikiHouse system ultimately proved to be more expensive than a traditional build.
According to Miranda, the cost of the completed homes was approximately 33% higher than a traditional build but she estimates if they were to build using WikiHouse again - taking on-board lessons learnt - the premium would reduce to 12% (Plowden, 2020). However, there is hope for the WikiHouse system to become a more financially competitive alternative to traditional build in the future. For this to happen, Miranda suggests improving efficiency of the assembly process, particularly with faster utility connections. Additional financial viability could also be achieved if the system were to be applied to larger sites. In regard to a life cycle costing approach, Miranda believes it is too early for SYHA to say whether the WikiHouse pilot will prove to be cheaper than a traditional build in the long-term.
A.Davis. ESR1
Read more
->

85 Social Housing Units in Cornellà
Created on 26-07-2024
An economic, social and environmental challenge
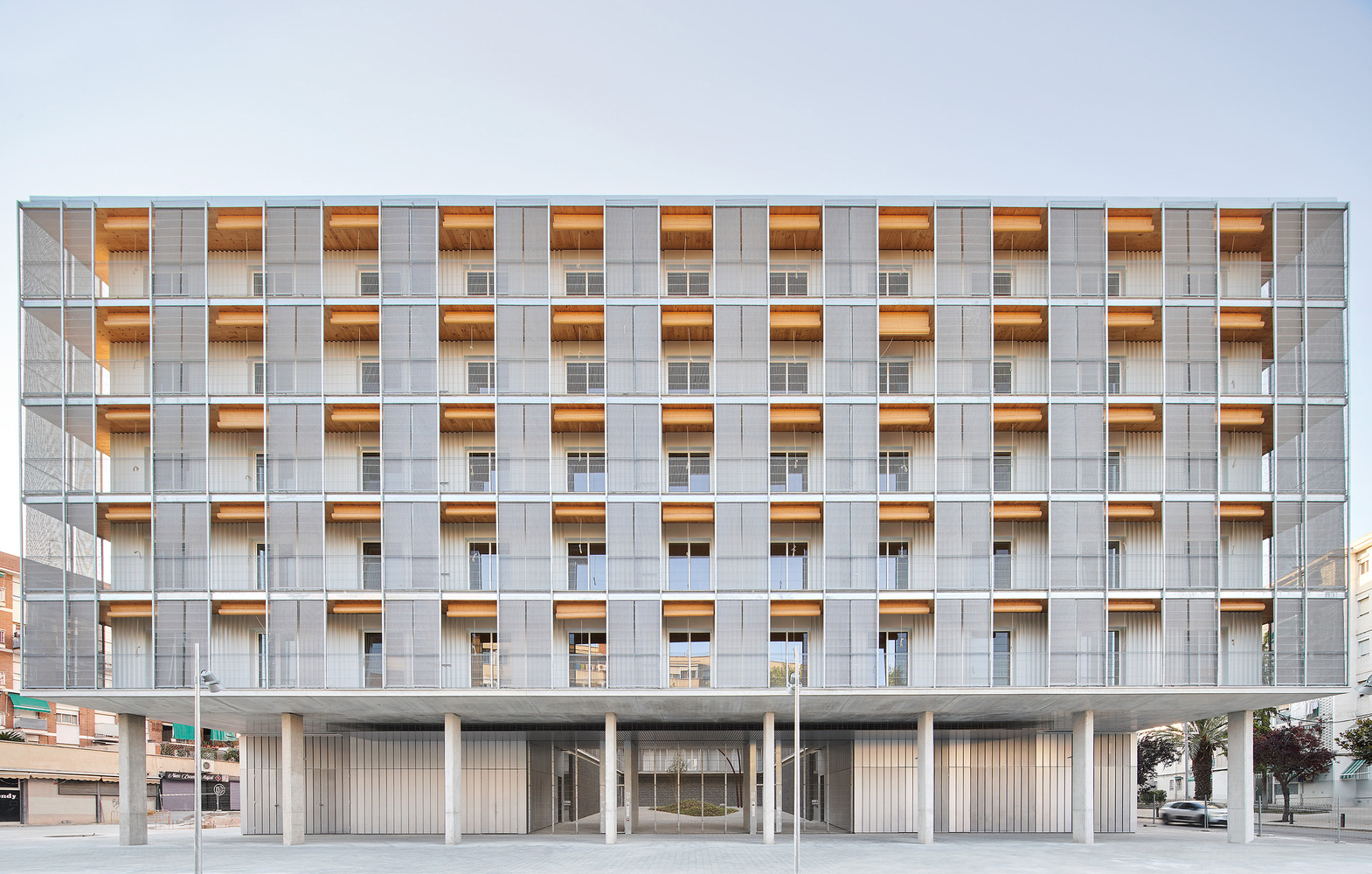
The architects Marta Peris and José Manuel Toral (P+T) faced the task of developing a proposal for collective housing on a site with social, economic, and environmental challenges. This social housing building won through an architectural competition organised by IMPSOL, a public body responsible for providing affordable housing in the metropolitan area of Barcelona. The block, located in the working-class neighbourhood of Sant Ildefons in Cornellà del Llobregat where the income per capita is €11,550 per year, was constructed on the site of the old Cinema Pisa. Although the cinema had closed down in 2012, the area remained a pivotal point for the community, so the social impact of the new building on the urban fabric and the existing community was of paramount importance.
The competition was won in 2017 and the housing was constructed between 2018 and 2020. The building, comprised of 85 social housing dwellings, covers a surface of 10,000m2 distributed in five floors. Adhering to a stringent budget based on social housing standards, the building offers a variety of dwellings designed to accommodate different household compositions. Family structures are heterogeneous and constantly evolving, with new uses entering the home and intimacy becoming more fluid. In the past, intimacy was primarily associated with a bedroom and its objects, but the concept has become more ambiguous, and now privacy lies in our hands, our phones, and other devices. In response to these emerging lifestyles, the architects envisioned the dwelling as a place to be inhabited in a porous and permeable manner, accommodating these changing needs.
This collective housing is organised around a courtyard. The housing units are conceived as a matrix of connected rooms of equal size, 13 m², totalling 114 rooms per floor and 543 rooms in the entire building. Dwellings are formed by the addition of 5 or 6 rooms, resulting in 18 dwellings per floor, which benefit from cross ventilation and the absence of internal corridors.
While the use of mass timber as an element of the construction was not a requisite of the competition, the architects opted to incorporate this material to enhance the building's degree of industrialisation. A wooden structure supports the building, made of 8,300 m² of timber from the Basque Country. The use of timber would improve construction quality and precision, reduce execution times, and significantly lower CO2 emissions.
De-hierarchisation of housing layouts
The project is conceived from the inside out, emphasising the development of rooms over the aggregation of dwellings. Inspired by the Japanese room of eight tatamis and its underlying philosophy, the architects aimed for adaptability through neutrality. In the Japanese house, rooms are not named by their specific use but by the tatami count, which is related to the human scale (90 x 180 cm). These polyvalent rooms are often connected on all four sides, creating great porosity and a fluidity of movement between them. The Japanese term ma has a similar meaning to room, but it transcends space by incorporating time as well. This concept highlights the neutrality of the Japanese room, which can accommodate different activities at specific times and can be transformed by such uses.
Contrary to traditional typologies of social housing in Spain, which often follow the minimum room sizes for a bedroom of 6, 8, and 10 m2 stipulated in building codes, this building adopted more generous room sizes by reducing living room space and omitting corridors. P+T anticipated that new forms of dwelling would decrease the importance of a large living room and room specialisation. For many decades, watching TV together has been a social activity within families. Increasingly, new devices and technologies are transforming screens into individual sources of entertainment. The architects determined that the minimum size of a room to facilitate ambiguity of use was 3.60 x 3.60m. Moreover, the multiple connections between spaces promote circulation patterns in which the user can wander through the dwelling endlessly. In this way, the rigid grid of the floor plan is transformed into an adaptable layout, allowing for various spatial arrangements and an ‘enfilade’ of rooms that make the space appear larger. Nevertheless, the location of the bathroom and kitchen spaces suggests, rather than imposes, the location of certain uses in their proximities. The open kitchen is located in the central room, acting as a distribution space that replaces the corridors while simultaneously making domestic work visible and challenging gender roles.
By undermining the hierarchical relation between primary and secondary rooms and eradicating the hegemony of the living room, the room distribution facilitates adaptability over time through its ambiguity of use. In this case, flexibility is achieved not by movable walls but by generous rooms that can be appropriated in multiple ways, connected or separated, achieving spatial polyvalency.
Degrees of porosity to enhance social sustainability
The architects believed that to enhance social sustainability, the building should become a support (in the sense of Open Building and Habraken’s theories) that fosters human relations and encounters between neighbours and household members. In this case there was no existing community, so to encourage the creation of such, the inner courtyard becomes the in-between space linking the public and the private realms, and the place from which the residents access to their dwellings. The gabion walls of the courtyard improve the acoustic performance of this semi-private space. P+T promote the idea of a privacy gradient between communal and the private spaces in their projects. In the case of Cornellà, the access to most dwellings from the terraces creates a connection between the communal and the private, suggesting that dwelling entrances act as filters rather than borders. Connecting this terrace to two of the rooms in a dwelling also provides the option for dual access, allowing the independent use of these rooms while favouring long-term adaptability. Inside the dwelling, the omission of corridors and the proliferation of connecting doors between spaces encourage human relationships and makes them indeterminate. This degree of connectedness between spaces and household members is defined by the degree of porosity chosen by the residents. At the same time, the porosity impacts the freedom to appropriate the space, giving greater importance to the furnishing of fixed areas within a space, such as the corners.
Reduction as an environmental strategy
The short distances defined by the non-hierarchical grid facilitated an optimal structural span for a timber structure. Although, the architects had initially proposed a wall-bearing CLT system, the design was optimised for economic viability by collaborating with timber manufacturers once construction started. This allowed the design team to assess the amount of timber and to research how it could be left visible, seeking to take advantage of all its hygrothermal benefits in the dwellings. It is evident that the greater the distance between structural supports, the more flexible the building is. But the greater this distance, the more material is needed for each structural component, and therefore the greater the environmental footprint. As a result of this collaborative optimisation process, two interior supporting rings were incorporated to the post and beam strategy, which significantly increased the adaptability of the building in the long term as well as halving the amount of timber needed. The façade and stair core continued to use wall-bearing CLT components, bracing the structure against wind and reducing the width of the pillars of the interior structure.
The building features galvanised steel connections between columns and girders, ensuring their continuity and facilitating the installation of services through open joints. Additionally, the high degree of industrialisation of the timber components, achieved through computer numerical control (CNC), optimised and ensured precise assembly. This mechanical connection between components permits the future disassembly if necessary, thereby contributing to a circular economy. To meet acoustic and fire safety requirements, a layer of sand and rockwool was placed on top of the CLT slabs of the flooring, between the timber and the screed, separating the dry and the humid works.
The environmental approach focuses on reducing building layers, drawing inspiration from vernacular architecture. However, unlike traditional building techniques which rely on manual labour, P+T employed prefabricated components to leverage the industry’s precision and reduce work, optimising the use of materials. This reductionist strategy enables them to maximise resources, cut costs, and lower emissions. As a result, the amount of timber actually used in the construction was half the amount proposed in the competition. Moreover, they minimised the number of elements and materials used. For example, an efficient use of folds and geometry eliminated the need for handrails, significantly reducing iron usage and lowering the building's overall carbon footprint.
The dwellings in Cornellà have garnered significant interest, receiving 25 awards from national and international organisations since 2021. Frequent visits from industry professionals, developers, architects, tourists and locals, demonstrate how this exemplary building, promoted by a public institution, may lead the way to more public and private developments that push the boundaries of innovation in future housing solutions.
C.Martín. ESR14
Read more
->