LiLa4Green
Created on 04-07-2023
Background
Over the last decades, international and national environmental policies have been designed and implemented to counteract the impact of the emerging climate change, this forcing many cities around the globe to adapt their urban environment and update their planning strategies. On a local level, targeted solutions to improve urban microclimates play a catalytic role on the sense of urban comfort, especially in densely built areas lacking green. Such nature-based and cost-effective solutions which provide environmental, social and economic benefits for resilience (European Commision Research and Innovation, n.d.), as well as comprehensive green and blue infrastructure strategies that promote the use of natural processes and vegetation to achieve landscape and water management benefits in an urban context (Victoria State Goverment Department of Environment Land Water and Planning, 2017) can counteract the effects of rising temperatures and provide resilience for cities and inhabitants (Roehr & Laurenz, 2008). However, their implementation and maintenance face many challenges, such as administrative limitations and lack of awareness or acceptance by the local stakeholders and residents (Hagen et al., 2021; Tötzer et al., 2019).
Working to address this challenge in a holistic manner, the LiLa4Green project, as part of the Smart Cities Initiative, aims to foster the implementation of nature-based solutions in the city of Vienna, by integrating a LL approach that focuses on social innovation and knowledge-sharing. The main goals of the project include the collaborative identification of challenges and potentials, the implementation of co-created solutions in the streetscape and the visualisation of the effects of potential solutions in a creative way to raise awareness and activate participants (Hagen et al., 2021).
The project is funded by the Climate and Energy Fund and is carried out by an interdisciplinary consortium consisting of research, academic and community partners. The project’s methodology has been tested in two residential neighbourhoods, ‘Quellenstraße Ost’ in the 10th district and ‘Kreta’ in the 14th district of Vienna. Both neighbourhoods are characterised by dense urban structures and insufficient public and green spaces, and their population consists predominantly of young, low-income immigrant groups who are poorly qualified and which suffer a high unemployment rate (Hagen et al., 2019).
Methodological Approach
The project was implemented along two parallel lines of work. The first refers to a scientific approach conducted by the research consortium. This initiated with the open space and microclimatic analysis of the areas, the results of which were seen in context with the climate of the whole city, concluding to the areas’ characterisation. A demarcation as ‘vulnerable with respect to densification’ (Tötzer et al., 2019, p. 3) reflects the high density and bioclimatic stress of the neighbourhood. The analysis offered valuable insights in identifying priority spots, i.e., small-scale heat islands, and was followed by discussions on greening potentials and recommendations about the areas’ needs and characteristics.
In parallel, a participatory process was initiated in the focus areas to inform the scientific findings on the most problematic locations in the neighbourhood based on the local knowledge and experience of residents and local stakeholders. At the same time, through the establishment of the LL as an alternative to top-down city planning strategies, residents moved from being information facilitators to co-creators.
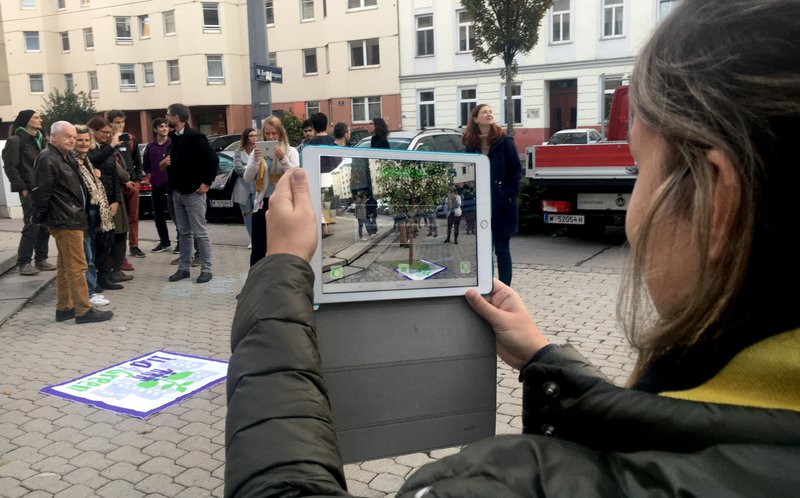
Following this approach of empowering residents to actively participate in the development of solutions that affect their living environment, the LL investigated ways to raise public awareness on mitigation and measures to facilitate citizens’ adaptation to climate change and to ensure a broad acceptance for the green-blue infrastructure among the general public, through the design and testing of multiple and diverse smart user participation and visualisation methods. A combination of innovative social science methods with the latest digital technology was put forward to facilitate the dissemination of information of the diverse functionalities of green and free spaces, testing also new methods of visualisation of the effects, such as Augmented and Virtual Reality, for more informed decisions (www.lila4green.at). Focusing further on the visibility and traceability (Hagen et al., 2021, p. 393) of the added value of the potential interventions, the monitoring phase included a combination of measurements, simulations and surveys, while in the assessment phase, innovative tools such as crowdsourcing and maps were employed to correlate multiple measurements such as costs and maintenance requirements.
Activities
The innovative methodology was tested in practice in a range of different activities organised by the LL that opened the research to citizens and stakeholders in an interactive format. The participatory process initiated with the LiLa4Green research team coming together to design the operation and context of the LL. The activities in the LL began with the ‘Start Workshop’, a knowledge-gathering meeting in which research team members and relevant stakeholders (representatives of municipal agencies and local institutions) came together to discuss constrains, potentials in the project area and the mutual benefits.
This introductory event was followed by the four cornerstones of the project, namely the ‘Green Workshops’ (GWs) that took place every 6 months and involved the research team, stakeholders and citizens. In preparation of each of these four events, a set of activities was organised on site, related to the objectives of the foregoing events, as well as the results of the previous ones. For instance, before the first Green Workshop that focused on ‘sharing information, building mutual understanding and establishing social connections’ (Tötzer et al., 2019, p. 5), the research team conducted on site activation activities which included the creation of a temporary space for conversations using pictures, signs and questions to approach the people passing by, and also engaging them through game-like activities of mapping and voting.
The first workshop started and concluded with a survey. The comparison of the answers of both surveys enabled the organisers to detect changes in the perception of participants on the topic and hence the success of the workshop in the transfer of knowledge. The workshop was organised in two parts that differentiated on the flow of knowledge from the research group to the participants and reversely, using posters, a memory set and a flyer as tools for communication.
Working on the feedback from the first workshop, the second event focused on the realisation of the first urban intervention, a parklet, that was developed as a student project at intended design studios at the TU Wien and then selected by the participants of the LL. Furthermore, using a smart interaction tool with AR technology on site, participants were given the chance to visualise and provide their feedback on potential greening interventions.
Having built trust between the participants and the research team, the third workshop aimed at the identification of the potential uses of the open space through gamification. The participants designed adaptation activities to respond to the scientifically identified conditions and further grounded their decisions to real restrictions, such as budget. In the same workshop, participants tested the AR tool that was further developed by the research team according to the feedback from the second workshop.
Finally, the fourth workshop dealt with the collective implementation of the developed proposals. Due to the pandemic outbreak the workshop was delivered in a digital format and the results were eventually implemented in the summer 2020.
Communication and Sharing Experience
Parallel to the workshops and activities, the consortium gave a great value to the communication and dissemination of LiLa4Green within and outside the focus areas by sending out a frequent newsletter and an Explain Video to attract and maintain participants’ motivation. Surveys and questionnaires were used to incorporate the feedback for the next stages, and experiences were shared via a website. Furthermore, the team created a brochure with the title “In 5 Schritten zum guten Klima” (LiLa4Green, n.d.) to summarise the smart participation methodology in five steps: 1. Prepare the ground and initiate the process, 2. Share knowledge and learn together, 3. Decide and create trust, 4. Designing the future in a playful way, and 5. Specify and implement together. Lastly, aiming to disseminate the knowledge and experiences with the scientific community, the research team actively participated in conferences, presentations, lectures and journals.
Acknowledgment
I would like to thank Tanja Tötzer, expert advisor at the Austrian Institute of Technology in Vienna and coordinator of the LiLa4Green project, for the inspiring discussion and generous insights that have helped to write about LiLa4Green.
A.Pappa. ESR13
Read more
->

La Borda
Created on 16-10-2024
The housing crisis
After the crisis of 2008, it became obvious that the mainstream mechanisms for the provision of housing were failing to provide secure and affordable housing for many households, especially in the countries of the European south such as Spain. It is in this context that alternative forms emerged through social initiatives. La Borda is understood as an alternative form of housing provision and a tenancy form in the historical and geographical context of Catalonia. It follows mechanisms for the provision of housing that differ from predominant approaches, which have traditionally been the free market, with a for-profit and speculative role, and a very low percentage of public provision (Allen, 2006). It also constitutes a different tenure model, based on collective instead of private ownership, which is the prevailing form in southern Europe. As such, it encompasses the notions of community engagement, self-management, co-production and democratic decision-making at the core of the project.
Alternative forms of housing
In the context of Catalonia, housing cooperatives go back to the 1960s when they were promoted by the labour movement or by religious entities. During this period, housing cooperatives were mainly focused on promoting housing development, whether as private housing developers for their members or by facilitating the development of government-protected housing. In most cases, these cooperatives were dissolved once the promotion period ended, and the homes were sold.
Some of these still exist today, such as the “Cooperativa Obrera de Viviendas” in El Prat de Llobregat. However, this model of cooperativism is significantly different from the model of “grant of use”, as it was used mostly as an organizational form, with limited or non-existent involvement of the cooperative members.
It was only after the 2008 crisis, that new initiatives have arisen, that are linked to the grant-of-use model, such as co-housing or “masoveria urbana”. The cooperative model of grant-of-use means that all residents are members of the cooperative, which owns the building. As members, they are the ones to make decisions about how it operates, including organisational, communitarian, legislative, and economic issues as well as issues concerning the building and its use. The fact that the members are not owners offers protection and provides for non-speculative development, while actions such as sub-letting or transfer of use are not possible. In the case that someone decides to leave, the flat returns to the cooperative which then decides on the new resident. This is a model that promotes long-term affordability as it prevents housing from being privatized using a condominium scheme. The grant -of -use model has a strong element of community participation, which is not always found in the other two models. International experiences were used as reference points, such as the Andel model from Denmark and the FUCVAM from Uruguay, according to the group (La Borda, 2020). However, Parés et al. (2021) believe that it is closer to the Almen model from Scandinavia, which implies collective ownership and rental, while the Andel is a co-ownership model, where the majority of its apartments have been sold to its user, thus going again back to the free-market stock.
In 2015, the city of Barcelona reached an agreement with La Borda and Princesa 49, allowing them to become the first two pilot projects to be constructed on public land with a 75-year leasehold. However, pioneering initiatives like Cal Cases (2004) and La Muralleta (1999) were launched earlier, even though they were located in peri-urban areas. The main difference is that in these cases the land was purchased by the cooperative, as there was no such legal framework at the time. This means that these projects are classified as Officially Protected Housing (Vivienda de Protección Oficial or VPO), and thus all the residents must comply with the criteria to be eligible for social housing, such as having a maximum income and not owning property. Also, since it is characterised as VPO there is a ceiling to the monthly fee to be charged for the use of the housing unit, thus keeping the housing accessible to groups with lower economic power. This makes this scheme a way to provide social housing with the active participation of the community, keeping the property public in the long term. After the agreed period, the plot will return to the municipality, or a new agreement should be signed with the cooperative.
The neighbourhood movement
In 2011, a group of neighbours occupied one of the abandoned industrial buildings in the old industrial state of Can Batlló in response to an urban renewal project, with the intention of preserving the site's memory (Can Batlló, 2020; Girbés-Peco et al., 2020). The neighbourhood movement known as "Recuperem Can Batlló" sought to explore alternative solutions to the housing crisis of the time. The project started in 2012, after a series of informal meetings with an initial group of 15 people who were already active in the neighbourhood, including members of the architectural cooperative Lacol, members of the labour cooperative La Ciutat Invisible, members of the association Sostre Civic and people from local civic associations. After a long process of public participation, where the potential uses of the site were discussed, they decided to begin a self-managed and self-promotion process to create La Borda. In 2014 they legally formed a residents’ cooperative and after a long process of negotiation with the city council, they obtained a lease for the use of the land for 75 years in exchange for an annual fee. At that time, the group expanded, and it went from 15 members to 45. After another two years of work, construction started in 2017 and the first residents moved in the following year.
The participatory process
The word “participation” is sometimes used as a buzzword, where it refers to processes of consultation or manipulation of participants to legitimise decisions, leading it to become an empty signifier. However, by identifying the hierarchies that such processes entail, we can identify higher levels of participation, that are based on horizontality, reciprocity, and mutual respect. In such processes, participants not only have equal status in decision-making, but are also able to take control and self-manage the whole process. This was the case with La Borda, a project that followed a democratic participation process, self-development, and self-management. An important element was also the transdisciplinary collaboration between the neighbours, the architects, the support entities and the professionals from the social economy sector who shared similar ideals and values.
According to Avilla-Royo et al. (2021), greater involvement and agency of dwellers throughout the lifetime of a project is a key characteristic of the cooperative housing movement in Barcelona. In that way, the group collectively discussed, imagined, and developed the housing environment that best covered their needs in typological, material, economic or managerial terms. The group of 45 people was divided into different working committees to discuss the diverse topics that were part of the housing scheme: architecture, cohabitation, economic model, legal policies, communication, and internal management. These committees formed the basis for a decision-making assembly. The committees would adapt to new needs as they arose throughout the process, for example, the “architectural” committee which was responsible for the building development, was converted into a “maintenance and self-building” committee once the building was inhabited. Apart from the specific committees, the general assembly is the place, where all the subgroups present and discuss their work. All adult members have to be part of a committee and meet every two weeks. The members’ involvement in the co-creation and management of the cooperative significantly reduced the costs and helped to create the social cohesion needed for such a project to succeed.
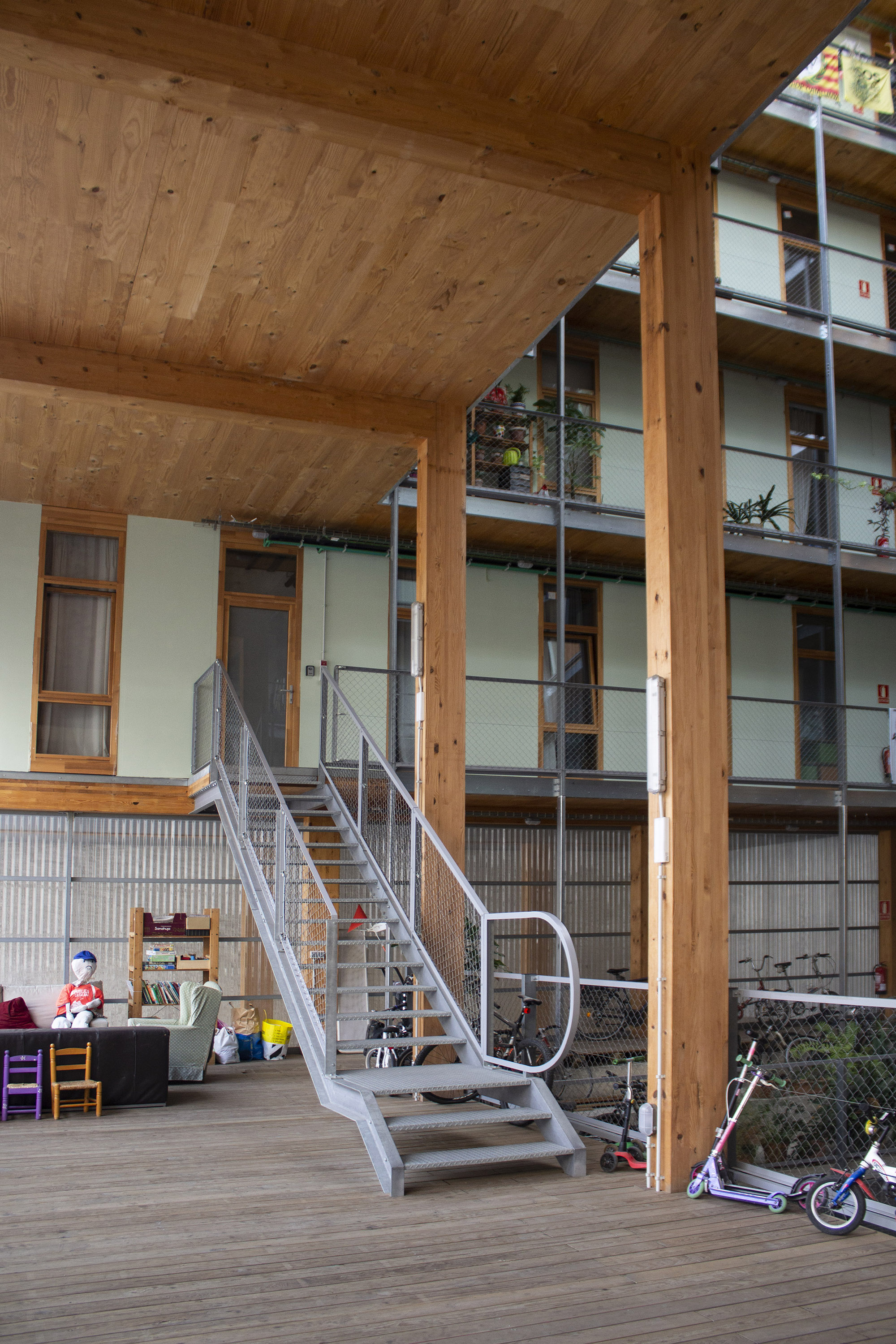
The building
After a series of workshops and discussions, the cooperative group together with architects and the rest of the team presented their conclusions on the needs of the dwellers and on the distribution of the private and communal spaces. A general strategy was to remove areas and functions from the private apartments and create bigger community spaces that could be enjoyed by everyone. As a result, 280 m2 of the total 2,950 m2 have been allocated for communal spaces, accounting for 10% of the entire built area. These spaces are placed around a central courtyard and include a community kitchen and dining room, a multipurpose room, a laundry room, a co-working space, two guest rooms, shared terraces, a small community garden, storage rooms, and bicycle parking. La Borda comprises 28 dwellings that are available in three different typologies of 40, 50 and 76 m2, catering to the needs of diverse households, including single adults, adult cohabitation, families, and single parents. The modular structure and grid system used in the construction of the dwellings offer the flexibility to modify their size in the future.
The construction of La Borda prioritized environmental sustainability and minimized embedded carbon. To achieve this, the foundation was laid as close to the surface as possible, with suspended flooring placed a meter above the ground to aid in insulation. Additionally, the building's structure utilized cross-laminated timber (CLT) from the second to the seventh floors, after the ground floor made of concrete. This choice of material had the advantage of being lightweight and low carbon. CLT was used for both the flooring and the foundation The construction prioritized the optimization of building solutions through the use of fewer materials to achieve the same purpose, while also incorporating recycled and recyclable materials and reusing waste. Furthermore, the cooperative used industrialized elements and applied waste management, separation, and monitoring. According to the members of the cooperative (LaCol, 2020b), an important element for minimizing the construction cost was the substitution of the underground parking, which was mandatory from the local legislation when you exceed a certain number of housing units, with overground parking for bicycles. La Borda was the first development that succeeded not only in being exempt from this legal requirement but also in convincing the municipality of Barcelona to change the legal framework so that new cooperative or social housing developments can obtain an “A” energy ranking without having to construct underground parking.
Energy performance goals focused on reducing energy demands through prioritizing passive strategies. This was pursued with the bioclimatic design of the building with the covered courtyard as an element that plays a central role, as it offers cross ventilation during the warm months and acts as a greenhouse during the cold months. Another passive strategy was enhanced insulation which exceeds the proposed regulation level. According to data that the cooperative published, the average energy consumption of electricity, DHW, and heating per square meter of La Borda’s dwellings is 20.25 kWh/m², which is 68% less, compared to a block of similar characteristics in the Mediterranean area, which is 62.61 kWh/m² (LaCol, 2020a). According to interviews with the residents, the building’s performance during the winter months is even better than what was predicted. Most of the apartments do not use the heating system, especially the ones that are facing south. However, the energy demands during the summer months are greater, as the passive cooling system is not very efficient due to the very high temperatures. Therefore, the group is now considering the installation of fans, air-conditioning, or an aerothermal installation that could provide a common solution for the whole building. Finally, the cooperative has recently installed solar panels to generate renewable energy.
Social impact and scalability
According to Cabré & Andrés (2018), La Borda was created in response to three contextual factors. Firstly, it was a reaction to the housing crisis which was particularly severe in Barcelona. Secondly, the emergence of cooperative movements focusing on affordable housing and social economies at that time drew attention to their importance in housing provision, both among citizens and policy-makers. Finally, the moment coincided with a strong neighbourhood movement around the urban renewal of the industrial site of Can Batlló. La Borda, as a bottom-up, self-initiated project, is not just an affordable housing cooperative but also an example of social innovation with multiple objectives beyond providing housing.
The group’s premise of a long-term leasehold was regarded as a novel way to tackle the housing crisis in Barcelona as well as a form of social innovation. The process that followed was innovative as the group had to co-create the project, which included the co-design and self-construction, the negotiation of the cession of land with the municipality, and the development of financial models for the project. Rather than being a niche project, the aim of La Borda is to promote integration with the neighbourhood. The creation of a committee to disseminate news and developments and the open days and lectures exemplify this mission. At the same time, they are actively aiming to scale up the model, offering support and knowledge to other groups. An example of this would be the two new cooperative housing projects set up by people that were on the waiting list for la Borda. Such actions lead to the creation of a strong network, where experiences and knowledge are shared, as well as resources.
The interest in alternative forms of access to housing has multiplied in recent years in Catalonia and as it is a relatively new phenomenon it is still in a process of experimentation. There are several support entities in the form of networks for the articulation of initiatives, intermediary organizations, or advisory platforms such as the cooperative Sostre Civic, the foundation La Dinamo, or initiatives such as the cooperative Ateneos, which were recently promoted by the government of Catalonia. These are also aimed at distributing knowledge and fostering a more inclusive and democratic cooperative housing movement. In the end, by fostering the community’s understanding of housing issues, and urban governance, and by seeking sustainable solutions, learning to resolve conflicts, negotiate and self-manage as well as developing mutual support networks and peer learning, these types of projects appear as both outcomes and as drivers of social transformation.
Z.Tzika. ESR10
Read more
->

DARE to Build, Chalmers University of Technology
Created on 04-07-2023
'DARE to build' is a 5–week (1 week of design – 4 weeks of construction) elective summer course offered at the Department of Architecture and Civil Engineering at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden. The course caters for master-level students from 5 different master programmes offered at the Architecture and Civil Engineering Department. Through a practice-based approach and a subsequent exposure to real-world problems, “DARE to build” aims to prove that “real change can be simultaneously made and learned (Brandão et al., 2021b, 2021a). The goal of this course is to address the increasing need for effective multidisciplinary teams in the fields of architecture, engineering and construction (AEC) in order to tackle the ever-growing complexity of real-world problems (Mcglohn et al., 2014), and the pervading lack of a strong pedagogical framework that responds effectively to this challenge. The two main foci of the “DARE to build” pedagogical model are: (1) to train students in interdisciplinary communication, to cultivate empathy and appreciation for the contributions of each discipline, to sharpen collaborative skills (Tran et al., 2012) and (2) to expose students in practice-based, real-world design projects, through a problem-and-project-based learning (PPBL) approach, within a multi-stakeholder learning environment (Wiek et al., 2014). This multi-stakeholder environment is situated in the municipality of Gothenburg and involves different branches and services (Stadsbyggnadskontoret, Park och Naturförvaltningen), local/regional housing companies (Familjebostäder, Bostadsbolaget), professionals/collectives operating within the AEC fields (ON/OFF Berlin, COWI), and local residents and their associations (Hyresgästföreningen, Tidsnätverket i Bergsjön).
Design & Build through CDIO
By showcasing that “building, making and designing are intrinsic to each other” (Stonorov et al., 2018, p. 1), students put the theory acquired into practice and reflect on the implications of their design decisions. Subsequently they reflect on their role as AEC professionals, in relation to local and global sustainability; from assessing feasibility within a set timeframe to the intangible qualities generated or channelled through design decisions in specific contexts. This hands-on learning environment applies the CDIO framework (conceive, design, implement, operate, http://www.cdio.org/), an educational framework developed in the MIT, with a particular focus on the “implementation” part. CDIO has been developed in recent years as a reforming tool for engineering education, and is centred on three main goals: (1) to acquire a thorough knowledge of technical fundamentals, (2) to sharpen leadership and initiative-taking skills, and (3) to become aware of the important role research and technological advances can play in design decisions (Crawley et al., 2014). Therefore, design and construction, combined with CDIO, offer a comprehensive experience that enables future professionals to assume a knowledgeable and confident role within the AEC sector.
Course structure
“DARE to build” projects take place during the autumn semester along with the “Design and Planning for Social Inclusion” (DPSI) studio. Students work closely with the local stakeholders throughout the semester and on completion of the studio, one project is selected to become the “DARE to build” project of the year, based on (1) stakeholder interest and funding capacity, (2) pedagogical opportunities and the (3) feasibility of construction. During the intervening months, the project is further developed, primarily by faculty, with occasional inputs from the original team of DPSI students and support from professionals with expertise relevant to a particular project. The purpose of this further development of the initial project is to establish the guidelines for the 1-week design process carried out within “DARE to build”.
During the building phase, the group of students is usually joined by a team of 10-15 local (whenever possible) summer workers, aged between 16-21 years old, employed by the stakeholders (either by the Municipality of Gothenburg or by a local housing company). The aim of this collaboration is twofold - to have a substantial amount of workforce on site and to create a working environment where students are simultaneously learning and teaching, therefore enhancing their sense of responsibility. “DARE to build” has also collaborated - in pre-pandemic times - with Rice University in Texas, so 10 to 15 of their engineering students joined the course as a summer educational experience abroad.
The timeline for each edition of the “DARE to build” project evolution can be schematically represented through the CDIO methodology, which becomes the backbone of the programme (adapted from the courses’ syllabi):
Conceive: Developed through a participatory process within the design studio “Design and Planning for Social Inclusion”, in the Autumn.
Design: (1) Teaching staff defines design guidelines and materials, (2) student participants detail and redesign some elements of the original project, as well as create schedules, building site logistical plans, budget logs, etc.
Implement: The actual construction of the building is planned and executed. All the necessary building documentation is produced in order to sustain an informed and efficient building process.
Operate: The completed built project is handed over to the stakeholders and local community. All the necessary final documentation for the operability of the project is produced and completed (such as-built drawings, etc.).
In both the design and construction process, students take on different responsibilities on a daily basis, in the form of different roles: project manager, site supervisor, communications officer, and food & fika (=coffee break) gurus. Through detailed documentation, each team reports on everything related to the project’s progress, the needs and potential material deficits on to the next day’s team. Cooking, as well as eating and drinking together, works as an important and an effective team-bonding activity.
Learning Outcomes
The learning outcomes are divided into three different sets to fit with the overall vision of “DARE to Build” (adapted from the course syllabi):
Knowledge and understanding: To identify and explain a project’s life cycle, relate applied architectural design to sustainability and to describe different approaches to sustainable design.
Abilities and skills: To be able to implement co-creation methods, design and assess concrete solutions, to visualise and communicate proposals, to apply previously gained knowledge to real-world projects, critically review architectural/technical solutions, and to work in multidisciplinary teams.
Assessment and attitude: To be able to elaborate different proposals on a scientific and value-based argumentation, to combine knowledge from different disciplines, to consider and review conditions for effective teamwork, to further develop critical thinking on professional roles.
The context of operations: Miljonprogrammet
The context in which “DARE to Build” operates is the so-called “Million Homes Programme” areas (MHP, in Swedish: Miljonprogrammet) of suburban Gothenburg. The MHP was an ambitious state-subsidised response to the rapidly growing need for cheap, high-quality housing in the post-war period. The aim was to provide one million dwellings within a decade (1965-1974), an endeavour anchored on the firm belief that intensified housing production would be relevant and necessary in the future (Baeten et al., 2017; Hall & Vidén, 2005). During the peak years of the Swedish welfare state, as this period is often described, public housing companies, with help from private contractors, built dwellings that targeted any potential home-seeker, regardless of income or class. In order to avoid suburban living and segregation, rental subsidies were granted on the basis of income and number of children, so that, in theory, everyone could have access to modern housing and full of state-of-the-art amenities (Places for People - Gothenburg, 1971).
The long-term perspective of MHP also meant profound alterations in the urban landscape; inner city homes in poor condition were demolished and entire new satellite districts were constructed from scratch triggering “the largest wave of housing displacement in Sweden’s history, albeit firmly grounded in a social-democratic conviction of social betterment for all” (Baeten et al., 2017, p. 637) . However, when this economic growth came to an abrupt halt due to the oil crisis of the 1970s, what used to be an attractive and modern residential area became second-class housing, shunned by the majority of Swedish citizens looking for a house. Instead, they became an affordable option for the growing number of immigrants arriving in Sweden between 1980 and 2000, resulting in a high level of segregation in Swedish cities. (Baeten et al., 2017).
Nowadays, the MHP areas are home to multi-cultural, mostly low income, immigrant and refugee communities. Media narratives of recent decades have systematically racialised, stigmatised and demonised the suburbs and portrayed them as cradles of criminal activity and delinquency, laying the groundwork for an increasingly militarised discourse (Thapar-Björkert et al., 2019). The withdrawal of the welfare state from these areas is manifested through the poor maintenance of the housing stock and the surrounding public places and the diminishing public facilities (healthcare centres, marketplaces, libraries, etc.) to name a few. Public discourse, best reflected in the media, often individualizes the problems of "culturally different" inhabitants, which subsequently "justifies" people's unwillingness to work due to the "highly insecure" environment.
In recent years, the gradual (neo)liberalisation of the Swedish housing regime has provided room for yet another wave of displacement, leaving MHP area residents with little to no housing alternatives. The public housing companies that own MHP stock have started to offer their stock to potential private investors through large scale renovations that, paired with legal reforms, allow private companies to reject rent control. As a result, MHP areas are entering a phase of brutal gentrification (Baeten et al., 2017).
Reflections
Within such a sensitive and highly complex context, both “DARE to Build”, and “Design & Planning for Social Inclusion” aspire to make Chalmers University of Technology an influential local actor and spatial agent within the shifting landscape of the MHP areas, thus highlighting the overall relevance of academic institutions as strong, multi-faceted and direct connections with the “real-world”.
Even though participation and co-creation methodologies are strong in all “Design and Planning for Social Inclusion” projects, “DARE to Build” has still some ground to cover. In the critical months that follow the selection of the project and up to the first week of design phase, a project may change direction completely in order to fit the pedagogical and feasibility criteria. This fragmented participation and involvement, especially of those with less power within the stakeholder hierarchy, risks leading to interventions in which local residents have no sense of ownership or pride, especially in a context where interventions from outsiders, or from the top down, are greeted with increased suspicion and distrust.
Overall “DARE to build” is a relevant case of context-based education which can inform future similar activities aimed at integration education in the community as an instrument to promote sustainable development.
Relevant “DARE to build” projects
Gärdsåsmosse uteklassrum: An outdoor classroom in Bergsjön conceptualised through a post-humanist perspective and constructed on the principles of biomimicry, and with the use of almost exclusively natural materials.
Visit: https://www.chalmers.se/sv/institutioner/ace/nyheter/Sidor/Nu-kan-undervisningen-dra-at-skogen.aspx
https://www.mynewsdesk.com/se/cowi/pressreleases/cowi-hjaelpte-goeteborgs-stad-foervandla-moerk-park-till-en-plats-att-ha-picknick-i-2920358
Parkourius: A parkour playground for children and teens of the Merkuriusgatan neighbourhood in Bergsjön. A wooden construction that employs child-friendly design.
Visit: https://www.sto-stiftung.de/de/content-detail_112001.html https://www.mynewsdesk.com/se/familjebostader-goteborg-se/pressreleases/snart-invigs-bergsjoens-nya-parkourpark-3111682
E.Roussou. ESR9
Read more
->

Marmalade Lane
Created on 08-06-2022
Background
An aspect that is worth highlighting of Marmalade Lane, the biggest cohousing community in the UK and the first of its kind in Cambridge, is the unusual series of events that led to its realisation. In 2005 the South Cambridgeshire District Council approved the plan for a major urban development in its Northwest urban fringe. The Orchard Park was planned in the area previously known as Arbury Park and envisaged a housing-led mix-use master plan of at least 900 homes, a third of them planned as affordable housing. The 2008 financial crisis had a profound impact on the normal development of the project causing the withdrawal of many developers, with only housing associations and bigger developers continuing afterwards. This delay and unexpected scenario let plots like the K1, where Marmalade Lane was erected, without any foreseeable solution. At this point, the city council opened the possibilities to a more innovative approach and decided to support a Cohousing community to collaboratively produce a brief for a collaborative housing scheme to be tendered by developers.
Involvement of users and other stakeholders
The South Cambridgeshire District Council, in collaboration with the K1 Cohousing group, ventured together to develop a design brief for an innovative housing scheme that had sustainability principles at the forefront of the design. Thus, a tender was launched to select an adequate developer to realise the project. In July 2015, the partnership formed between Town and Trivselhus ‘TOWNHUS’ was chosen to be the developer. The design of the scheme was enabled by Mole Architects, a local architecture firm that, as the verb enable indicates, collaborated with the cohousing group in the accomplishment of the brief. The planning application was submitted in December of the same year after several design workshop meetings whereby decisions regarding interior design, energy performance, common spaces and landscape design were shared and discussed.
The procurement and development process was eased by the local authority’s commitment to the realisation of the project. The scheme benefited from seed funding provided by the council and a grant from the Homes and Communities Agency (HCA). The land value was set on full-market price, but its payment was deferred to be paid out of the sales and with the responsibility of the developer of selling the homes to the K1 Cohousing members. Who, in turn, were legally bounded to purchase and received discounts for early buyers.
As relevant as underscoring the synergies that made Marmalade Lane’s success story possible, it is important to realise that there were defining facts that might be very difficult to replicate in order to bring about analogue housing projects. Two major aspects are securing access to land and receiving enough support from local authorities in the procurement process. In this case, both were a direct consequence of a global economic crisis and the need of developing a plot that was left behind amidst a major urban development plan.
Innovative aspects of the housing design
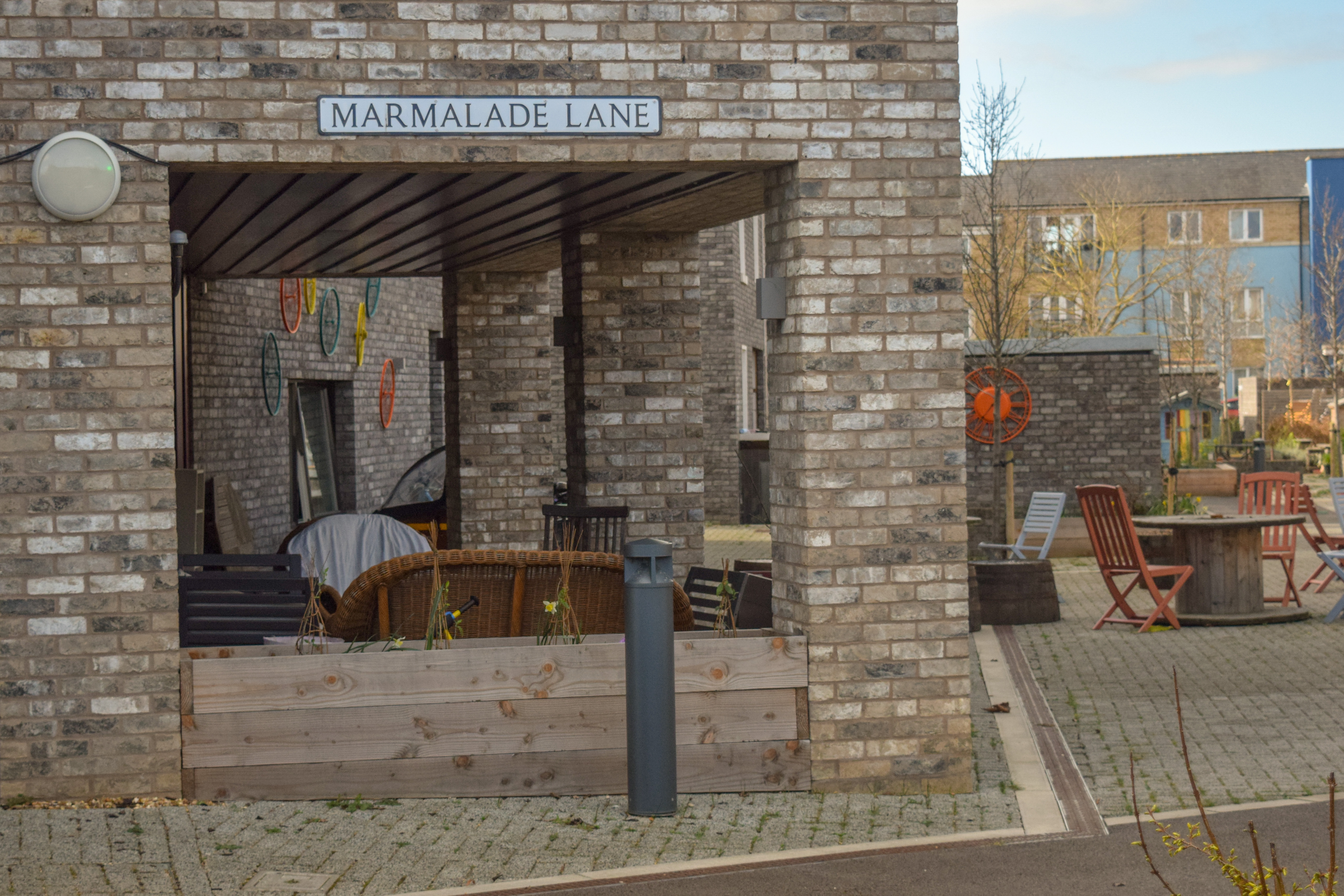
Spatially speaking, the housing complex is organised following the logic of a succession of communal spaces that connect the more public and exposed face of the project to the more private and secluded intended only for residents and guests. This is accomplished by integrating a proposed lane that knits the front and rear façades of some of the homes to the surrounding urban fabric and, therefore, serves as a bridge between the public neighbourhood life and the domestic everyday life. The cars have been purposely removed from the lane and pushed into the background at the perimeter of the plot, favouring the human scale and the idea of the lane as a place for interaction and encounters between residents. A design decision that depicts the community’s alignment with sustainable practices, a manifesto that is seen in other features of the development process and community involvement in local initiatives.
The lane is complemented by numerous and diverse places to sit, gather and meet; some of them designed and others that have been added spontaneously by the inhabitants offering a more customisable arrangement that enriches the variety of interactions that can take place. The front and rear gardens of the terraced houses contiguous to the lane were reduced in surface and remained open without physical barriers. A straightforward design decision that emphasises the preponderance of the common space vis-a-vis the private, blurring the limits between both and creating a fluid threshold where most of the activities unfold.
The Common House is situated adjacent to the lane and congregates the majority of the in-doors social activities in the scheme, within the building, there are available spaces for residents to run community projects and activities. They can cook in a communal kitchen to share both time and food, or organise cinema night in one of the multi-purpose areas. A double-height lounge and children's playroom incite gathering with the use of an application to organise easily social events amongst the inhabitants. Other practical facilities are available such as a bookable guest bedroom and shared laundry. The architecture of its volume stands out due to its cubic-form shape and different lining material that complements its relevance as the place to convene and marks the transition to the courtyard where complementary outdoor activities are performed. Within the courtyard, children can play without any danger and under direct supervision from adults, but at the same time enjoy the liberty and countless possibilities that such a big and open space grants.
Lastly, the housing typologies were designed to recognise multiple ways of life and needs. Consequently, adaptability and flexibility were fundamental targets for the architects who claim that units were able to house 29 different configurations. They are arranged in 42 units comprehending terraced houses and apartments from one to five bedrooms. Residents also had the chance to choose between a range of interior materials and fittings and one of four brick colours for the facade.
Construction and energy performance characteristics
Sustainability was a prime priority to all the stakeholders involved in the project. Being a core value shared by the cohousing members, energy efficiency was emphasised in the brief and influenced the developer’s selection. The Trivselhus Climate Shield® technology was employed to reduce the project’s embodied and operational carbon emissions. The technique incorporates sourced wood and recyclable materials into a timber-framed design using a closed panel construction method that assures insulation and airtightness to the buildings. Alongside the comparative advantages of reducing operational costs, the technique affords open interior spaces which in turn allow multiple configurations of the internal layout, an aspect that was harnessed by the architectural design. Likewise, it optimises the construction time which was further reduced by using industrialised triple-glazed composite aluminium windows for easy on-site assembly. Furthermore, the mechanical ventilation and heat recovery (MVHR) system and the air source heat pumps are used to ensure energy efficiency, air quality and thermal comfort. Overall, with an annual average heat loss expected of 35kWh/m², the complex performs close to the Passivhaus low-energy building standard of 30kWh/m² (Merrick, 2019).
Integration with the wider community
It is worth analysing the extent to which cohousing communities interact with the neighbours that are not part of the estate. The number of reasons that can provoke unwanted segregation between communities might range from deliberate disinterest, differences between the cohousing group’s ethos and that one of the wider population, and the common facilities making redundant the ones provided by local authorities, just to name a few. According to testimonies of some residents contacted during a visit to the estate, it is of great interest for Marmalade Lane’s community to reach out to the rest of the residents of Orchard Park. Several activities have been carried out to foster integration and the use of public and communal venues managed by the local council. Amongst these initiatives highlights the reactivation of neglected green spaces in the vicinity, through gardening and ‘Do it yourself’ DIY activities to provide places to sit and interact. Nonetheless, some residents manifested that the area’s lack of proper infrastructure to meet and gather has impeded the creation of a strong community. For instance, the community centre run by the council is only open when hired for a specific event and not on a drop-in basis. The lack of a pub or café was also identified as a possible justification for the low integration of the rest of the community.
Marmalade Lane residents have been leading a monthly ‘rubbish ramble’ and social events inviting the rest of the Orchard Park community. In the same vein, some positive impact on the wider community has been evidenced by the residents consulted. One of them mentioned the realisation of a pop-up cinema and a barbecue organised by neighbours of the Orchard Park community in an adjacent park. Perhaps after being inspired by the activities held in Marmalade Lane, according to another resident.
L.Ricaurte. ESR15
Read more
->

Navarinou Park
Created on 03-10-2023
Background
The neighbourhood of Exarcheia, where the park is located, is one of the most – if not the most– politically active areas in Athens and is traditionally home to intellectuals and artists. Since the 1970s, it has been in the centre of social movements, serving as a breeding ground for leftist, anarchist and antifascist grassroots and alternative cultural practices (Chatzidakis, 2013). Given its location in the centre of Athens, the neighbourhood is lacking green and open spaces.
The site of the park has a long history of negotiations regarding ownership and use, dating back to the 1970s. During that time, the Technical Chamber of Greece (TEE) purchased the 65-year-old medical clinic with the purpose of demolishing it and constructing its central offices. Although the building was eventually demolished in the 1980s, TEE never constructed its offices. In the 1990s, the site was offered as part of an exchange between the TEE and the Municipality of Athens for the development of a green space, but this agreement did not materialise. Instead, the TEE leased the plot for private use, and turned it into an open-air parking space (Frezouli, 2016).
The termination of the lease in 2008 coincided with a major social movement triggered by the assassination of a 15-year-old boy, Alexis Grigoropoulos, at the hands of the police. This tragic incident took place in December of the same year, just a few streets away from the site and led to uprisings in many Greek cities and neighbourhoods as citizens demanded the right to life, freedom, and the city through protests and illegal occupations. In response to the rumours about the site’s future construction, the Exarcheia Residents’ Initiative, in collaboration with many grassroots movements, used digital means to issue a collective call for action to reclaim the plot as an open green space. On 7th March 2009, tens of people from the neighbourhood and around Athens occupied the plot and created the 'Self-managed Navarinou and Zoodochou Pigis Park' (Frezouli, 2016; pablodesoto, 2010)
The park as an urban commons urban commons resource
The operation and development of the park, in terms of its uses and infrastructure, is collectively shaped by the appropriating community of commoners, consisting of activists and local residents, without any contributions from the state, municipal or private organisations. Hence the activities and interventions within the park are evolving with the joint efforts and time, work, skills and financial resources of the commoners.
In this regard, the transformation of the space from a parking lot into its present form has followed a dynamic process, that keeps adapting to the changing resources, needs and challenges created by the social and urban circumstances. The initial intervention involved replacing the concrete ground with soil and planting flowers and trees donated by the community. Subsequently, a small playground and seating areas were constructed, forming an open amphitheatre (Parko Navarinou Initative, 2018b). This infrastructure served as a base for organising public events such as cultural activities, public discussions, live concerts, film projections, and children’s activities. At a later stage, educational workshops on agriculture were also introduced (Frezouli, 2016). Many of the activities brought about spatial transformations within the park, including the creation of community gardens or sculptures, murals and installations.
In its most recent phase, the park has been transformed into a “big playground” for all the residents housing a variety of greenery, such as the urban gardens, as well as seating and gathering urban furniture, including benches and tables. The park now features several playground equipment suitable for both children and adults, such as swings, playing structures, a basketball court, and a ping pong table. Additionally, safety has been enhanced by improving the lighting and adding a fence (Parko Navarinou Initative, 2018a).
Commoners and commoning
To thrive as a bottom-up initiative, the operation and governance of the park are based on several forms of mobilisation that extend beyond the initial public space occupation. Among the various forms of commoning undertaken, activism, collective action, network creation and co-governance have been vital for Navarinou Park. These social processes have been supported by other participatory or community-based practices, such as public campaigns, co-construction and co-creation activities (Frezouli, 2016).
Since its beginning, the initiative has established an open assembly as the main instrument for decision-making on operational and infrastructural matters related to the park. This ensures that the park remains a shared resource, fostering a sense of belonging and strong bonds among the commoners. The assembly sets the rules and practises that constitute the institutional arrangements of the park, following a governance model based on horizontal democratic processes driven by the principles of self-management, anti-hierarchy and anti-commodification. The assembly is open to any individual or group that wishes to participate. However, throughout the park’s lifetime, only a small core of people remains permanently committed to the initiative. This groups is cohesive in terms of social incentives, activist ideals, and social capital, which reduces conflicts during decision-making processes (Arvanitidis & Papagiannitsis, 2020).
However, beyond addressing issues such as maintenance, organisation of events and infrastructure interventions, the assembly has been confronted with several challenges of both internal and external character, necessitating adaptability and rule-setting. One key challenge is the continuous commitment required for attending meetings and carrying out the daily tasks, which relies entirely on voluntary engagement. The gradual decrease in engagement, reaching its peak in early 2018 and even threatening the park’s survival, prompted the core team to seek new forms of communication and involvement to attract more residents to use and engage with the space. (Arvanitidis & Papagiannitsis, 2020). The idea that emerged focused on addressing the lack of play-areas in the neighbourhood by transforming the park into a large playground that would appeal to families, parents, children and the elderly. This vision was realised through a successful crowdfunding campaign (Parko Navarinou Initative, 2018a) that used the moto “play, breath, discuss, blossom, reclaim, live” to convey the key functions of the park.
Another significant challenge, especially during the first years of the initiative, was external delinquent behaviour, including vandalism, drug trafficking, and problems with the police (Avdikos, 2011). After several negotiations, the assembly decided to install a fence around the park to improve the monitoring and maintenance of the space while still keeping it open to everyone during operational hours and activities.
Impact & Significance
Navarinou Park is considered to be a successful example of the bottom-up transformation of an urban void into an urban commons among scholarly discourses (Arvanitidis & Papagiannitsis, 2020; Daskalaki, 2018; Frezouli, 2016; pablodesoto, 2010). It not only provides environmental benefits delivered through high quality green spaces, along with a variety of social and cultural activities for the residents of Exarcheia but, most significantly, it has "motivated and empowered residents, offering a great sense of pride and providing incentives for enhancing social capital and social inclusion, community resilience, collective learning and action"(Daskalaki, 2018, p. 162). The park demonstrates a successful example of urban commons in continuous growth, where social capital and solidarity are the motivating goals that drive both collective management and the ability to overcome challenges over time:
“If there is one thing that motivates us to move forward, it is the impact of our endeavour not only in theory but in practice: in the constructive transformation of behaviours, awarenesses, practices and everyday lives. It is up to us to seize the new opportunities that open up before us. If we ourselves do not struggle to create the utopias we imagine, they will never exist”. (Parko Navarinou Initative, 2018a)
A.Pappa. ESR13
Read more
->

Die Baupiloten Berlin
Created on 29-07-2024
Overview
The impetus behind the creation of Baupiloten was the growing concern within German architectural associations about the education offered at architecture faculties. At the turn of this century, architectural education in Germany was severely criticised on the basis of its perceived distance from the “practical necessities of the profession”, with students training only in abstract projects that would never be built (Hofmann, 2004, p. 115). The founder and leader, Susanne Hofmann, has been involved both in practice and academia/research and is a firm believer that intertwining these two pillars offers much broader opportunities for students to learn through direct exposure in reality-based conditions, thus bridging the gap between architectural education and professional practice.
In the spirit of restructuring prevalent architectural curricula, the Studienreformprojekt at TU Berlin set forth the following goals, which Baupiloten set to accomplish (Hofmann, 2004, p. 117):
Develop a connection between practice and research-oriented learning through building projects
Provide opportunities to explore the interdependences between the design and building process
Enhance interdisciplinary connections between the different fields of expertise that can be found in TU Berlin
Foster the project motivation and responsibility of students by allowing them to be a part of every stage, from the conception to the construction stages
Encourage students to test their ideas in a real, tangible project
Participation and atmosphere
Participation of non-experts
One of the core tenets of Baupiloten is the recognition of user knowledge as equally important to that of the “experts”. Users possess a specific kind of experiential, contextualised expertise on spatial arrangement, which, as Hofmann posits, becomes an invaluable source of information that can only be tapped into through real, active inclusion in the design process (Hofmann, 2019). Therefore, participation becomes a central focus in the Baupiloten approach, creating impactful and meaningful designs whose components can be traced back to the actual needs and desires of the people they design for.
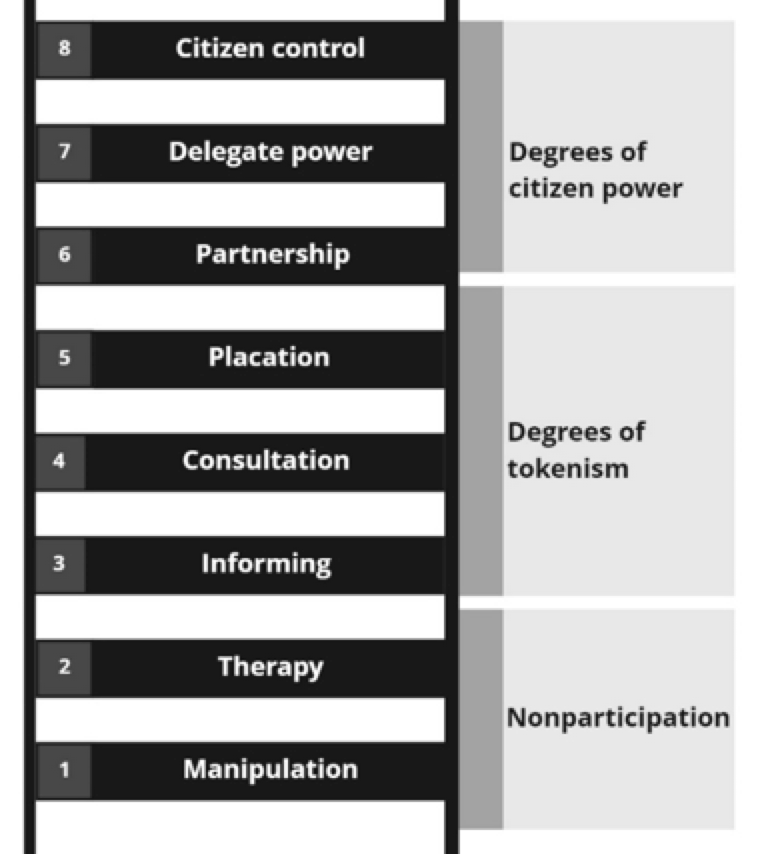
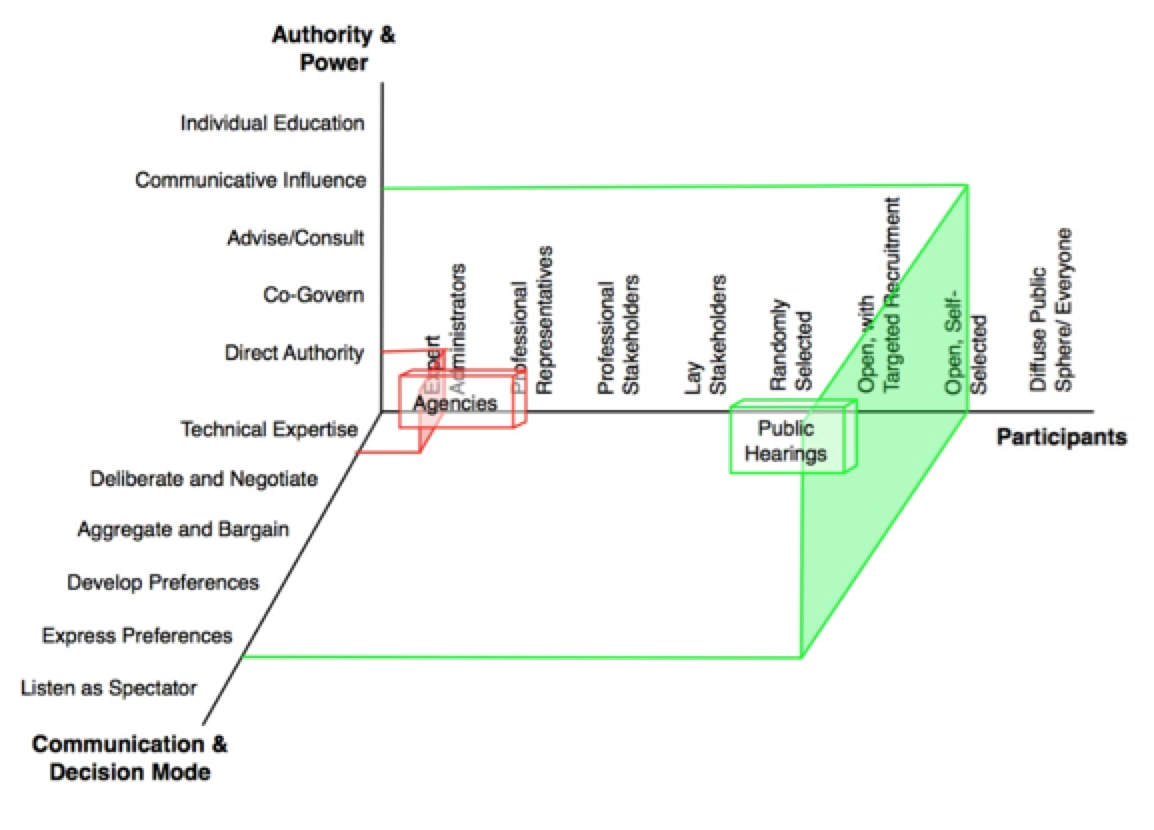
While participation has often been criticised on the basis of responsibility and accountability diffusion, superficiality and risks of manipulation and tokenistic practices (Miessen, 2010), Hofmann argues that participation can (1) amplify creativity and invention, both through the multiple perspectives entering the discussion and through the need for creative solutions to facilitate the dialogue (e.g. discussion game design). It can (2) reduce costs and shorten the timeframe, as visions for the desired interventions are jointly shaped, so that time and cost estimations can be measured and planned with fewer amendments during the process. It can (3) promote social cohesion, through the co-existence and interaction of diverse groups. Finally, it can (4) ensure architectural quality of the finished product by securing a clear correspondence between the final design and the user needs (Hofmann, 2018).
While the clear-cut binary of “expert” and “layperson” slowly dissolves, flexibility becomes even more crucial when it comes to the role of the architect; facilitating and moderating skills arise as equally crucial during the process, and effective communication becomes the key to a successful process. This does not mean that space design and production should no longer be the core competence of an architect, but rather that it needs to be expanded and renegotiated to fit the needs of a diverse project team (Hofmann, 2019).
Therefore, one of the focal questions that Baupiloten seeks to answer is how “can communication between citizens, architects, authorities, business, social movements – everyone – be facilitated without a loss of quality?” (Hofmann, 2018, p. 117)
Perception of atmospheres as a means of communication
Within Baupiloten, “atmosphere" is understood as the subjective perception of a space's emotional and sensory qualities, which significantly influences user experience. This concept extends beyond mere aesthetics, encompassing the interplay of light, sound, texture, and spatial arrangements to create a cohesive emotional impact. Baupiloten utilises this understanding of atmosphere to facilitate the communication of design intentions and foster a collaborative co-design process. By articulating the desired atmospheric qualities, designers can convey complex ideas and emotions that are otherwise challenging to express through conventional architectural drawings or technical specifications.
Atmosphere articulation becomes a central tool in the co-design process, engaging users and stakeholders in the creation of a shared vision for the space. Through workshops, mock-ups, and immersive simulations, participants experience and respond to the proposed atmospheres, providing valuable feedback that informs the design development. This collaborative approach ensures that the final design resonates with users' needs and preferences, creating spaces that are not only functional but also emotionally engaging. By focusing on atmospheres, Baupiloten bridges the gap between technical design and human experience, fostering a more inclusive and participatory design process that enhances the overall quality and impact of the built environment (Hofmann, 2019).
Methodology and learning objectives
Methodology
Baupiloten follows a 4-stage methodology aimed at kickstarting the dialogue and subsequent collaborative design process among participating stakeholders (Hofmann, 2018):
Team-building: raising awareness and building a common ground for communication through dialogue and other interactive activities.
Users’ everyday life: observing and recording daily activities.
“Wunschforschung”: researching the needs and desires of the users in a systematic manner.
Feedback: optimising the design according to comments received by the participants.
This methodology includes three broad, equally important categories of participating stakeholders:
Users: the “citizen experts”, bringing the knowledge of the everyday life to the table
Clients: the individuals or entities who commission the project and define the financial constraints that the design and construction must adhere to.
Architects: professionals and experts whose role is to facilitate and moderate the interactions, optimising their level of involvement to meet the process’s requirements.
Projects begin with students developing parallel designs. After a few weeks, the ideas are scrutinised to identify which concepts should be further refined, and students proceed to create and discuss various versions, ultimately selecting the final concept. Once a project is deemed convincing, it is divided into distinct packages for each student to develop independently. These design packages are intended to be sufficiently challenging yet comprehensible enough for the students to carry out successfully.
Overall, projects are divided by planning stages, potentially spanning through multiple semesters, and their schedule is aligned with the academic year to ensure professional management and relevance to real-world contexts. Instead of presenting related topics and themes as abstracted theory within the project (e.g. building regulations, lighting design principles, structural engineering, etc.), students are encouraged to learn experientially, through on-demand contextualising knowledge from related fields and topics as they progress on the project at hand (Hofmann, 2004).
Learning objectives
The learning objectives are separated into two main categories, as follows (Hofmann, 2004):
Fostering professional competences related to the different stages of a project
Developing design skills
Training in designing from concept to construction detail
Learning about cost-calculation and budgeting
Developing self-reflexive and assessment skills and methods
Enhancing interpersonal, communication and teamwork-related skills
Cultivating management skills
Learning how to interact with the various stakeholders involved in a project (clients, public authorities, craftsmen, manufacturers and building contractors)
Learning how to prepare and give effective presentations
Training in performing at and leading client meetings
Notable projects
Erika Mann Elementary School (or “the snuffle of the silver dragon”)
The Erika Mann Elementary School in the Wedding area of Berlin. When the phase 1 of the project was initiated (2003), Wedding had a high unemployment rate and a significant migrant population from non-German-speaking backgrounds. Baupiloten was tasked with initiating a collaborative design process, aiming to enhance the school premises with additional learning and living environments. The aim was to improve the quality of life within the school and make it an important hub for the whole neighbourhood.
Operating under the principle of “Form follows kids’ fiction”, the school students engaged with Baupiloten students and tutors in a series of design workshops spanning two phases: the first taking place in 2003 and the second in 2008, following the extension of the school’s operating hours to all-day. These workshops resulted in a proposal featuring a series of interventions designed to contrast the rigidness of the school’s hallways by creating “fantastical and poetic worlds, culminating in the fictive "Snuffle of the Silver Dragon"”(ArchDaily, 2009).
Kotti 3000
Kotti 3000 (alternatively, Neighbourhood 3000), is an interview tool and game specifically designed to encourage participation from people, such as migrants, whose voices, opinions and desires are often overlooked.
In this game, the players begin with a map of the neighbourhood. Through discussion and interaction, they can place a wide range of pictogram stickers on it. Each pictogram represents a type of urban equipment or function and “costs” a varying amount of points (e.g. cinema=300 points, vegetable garden=100 points). The overarching goal is to collaboratively “spend” the 3,000 points available to the participants on different types of interventions based on their needs and desires (Baupiloten, n.d.; Khafif, 2024).
E.Roussou. ESR9
Read more
->

Broadwater Farm Urban Design Framework
Created on 26-07-2024
The Broadwater Farm Estate
The estate, built in the full swing of modernism, is a paragon of the movement’s defining characteristics. The building density is notably high compared to the surrounding single-family terraced houses. There is a clear separation between vehicles and pedestrians, with platforms and deck accesses. The ensemble comprises twelve high-rise precast concrete blocks and towers, which extend over a public-owned site of 18 hectares, which is unusually large by today’s standards. Facilities were also provided for residents, offering them the essential amenities. Upon completion in the early 1970s, the estate comprised 1,063 flats and was home to between 3,000 and 4,000 residents.
As was the case with numerous other modernist housing estates across the country, Broadwater Farm was significantly affected by the seminal work of Alice Coleman, Utopia on Trial (1985) on the concept of “defensible space”. Proponents of this theory posited that design had a deterministic impact on crime rates and social malaise in low-income urban communities. Although Coleman's study faced harsh criticism from academics for its questionable methodology and oversimplification of complex social problems (Cozens & Hillier, 2012; Lees & Warwick, 2022), her recommendations led to the implementation of a multi-million-pound government-funded programme for remedial works in thousands of social housing blocks nationwide; known as the DICE (Design Improvement Controlled Experiment) project. Broadwater Farm was targeted by the programme after it attracted considerable attention following the serious riots that occurred at the estate in 1985 (Stoddard, 2011). A number of initiatives were undertaken with the objective of regenerating and improving the quality of the built environment, with the earliest works beginning in 1981. Under the DICE project, a significant number of the overpass decks that connected the estate on the first floor were demolished on the grounds that they were conducive to the formation of poorly lit and isolated areas that were facilitating criminal activity and anti-social behaviour (Severs, 2010).
In the wake of the Grenfell Tower tragedy, new fire safety regulations and inspections have been introduced, resulting in two blocks of flats being deemed unfit for habitation (BBC, 2022). The Large Panel System (LPS), which was commonly used in the 1960s, has been identified as the primary cause for the demolition of the Tangmere and Northolt blocks due to the significant risk of collapse in the event of a fire. These essential repairs will be part of the largest refurbishment project ever undertaken in the estate. It will comprise a combination of retrofitting, redevelopment and infill, resulting in an increase in the number of housing units and a significant enhancement of the urban layout and public spaces across its 83,000 sq. m.
The Urban Design Framework (UDF) is a comprehensive document that sets out a series of actionable and tangible improvements for the estate. Produced by Karakusevic Carson Architects (2022) and commissioned by the Haringey Borough Council, the UDF serves as a masterplan for the ongoing regeneration of the estate. This document is the result of an extensive stakeholder involvement process. It proposes a series of five urban strategies that, taken together, provide a blueprint for holistic regeneration. These strategies account for the short, medium and long-term development of both the estate and its community.
Given the substantial size of the complex, the scale of the surrounding neighbourhood, and the intricate web of relationships within it, long-term planning holds significant importance. These aspects were emphasised through the proposed interventions that enhance the connections between the dwellings and the urban context. The impact of the estate on the surrounding area and the need for a cohesive urban landscape are addressed through designs that integrate the estate into the city fabric, rather than isolating it. The improvement plan includes the construction of new residential units through the redevelopment of the blocks earmarked for demolition and the refurbishment of the remaining blocks. The architectural firm has developed a "bank of projects," a comprehensive repository of proposed interventions arising from engagement with the community as well as a site analysis, which is organised around five core principles: streets, open spaces, ground floors, character, and homes.
Resident engagement
The inhabitants were actively involved in the creation of the UDF. A series of community engagement events, held between 2020 and 2021, provided a platform to gather the voices of residents and enabled planners to better understand their aspirations and needs, identify the key improvements required, and initiate the design process that would incorporate their views into the masterplan. This process was complemented by the establishment of the Community Design Group (CDG), formed by residents and community members who not only expressed a desire, but also demonstrated the capacity, to assume a more active role in the design process. In addition, the council has set up a website that documents and displays the schedule, events, latest news and updates on the ongoing regeneration process. This website provides comprehensive information for residents, the general public, and any interested parties seeking to gain insight into the current status of Broadwater Farm.
Placemaking strategy
In contrast to pervasive narratives about the flawed design of council estates, the spatial qualities and existing sense of belonging within the community were identified as the starting points for the placemaking strategy. The original configuration of the estate was conceived around community facilities and courtyards, which have been retained, augmented, formalised, and linked by a circuit of pedestrian and cycle paths. The deficiencies of the original design, such as the anonymous and segregated ground floor, have been addressed by establishing a network of public spaces that prioritise human scale and facilitate movement throughout the estate. These new public spaces facilitate social interaction, providing areas of activity complemented by indoor amenities and spaces for local retailers. In this way, the ground level becomes an anchor for diverse activities aimed at enhancing the sense of security.
The masterplan revolves around five principles which in turn incorporate a series of strategies:
1. Safe and Healthy Streets: The improved design shifts away from 'streets in the sky' to enhance street accessibility. It promotes intermodal transport with a new bus route into the estate and the addition of cycle lanes. The road network within the estate has been simplified to be more efficient and encourage walking. A "green" street connects key community facilities and green spaces. Overall wayfinding is enhanced through better street lighting, improved block entrances, and designated car-free areas. Part and parcel of reactivating the ground floor is creating opportunities for new activities through a redesign aimed at more efficient parking solutions to meet current needs.
2. Welcoming + Inclusive Open Spaces: Although the estate features several courtyards and open areas, residents have expressed a feeling of being in a “concrete jungle”, as noted in the community brief. The proposed improvements focused on enhancing the existing courtyards to ensure accessibility and facilitate various activities. In addition, a new community park is planned at the heart of the estate as part of the redeveloped area, designed to be a versatile and welcoming space for current and future residents alike. A hierarchy of shared and public spaces has been redesigned to create a seamless transition into and out of the estate. This seamless and unified experience of the public realm is enabled by specific elements such as play areas and seating that allow people of all ages to socialise and interact in an informal yet purposeful manner.
Workshops were conducted with specific population groups, including young women and girls or older residents, to ensure that the future estate will be as inclusive as possible. Key topics such as perceived safety in the communal areas, activities and sports facilities, as well as overall design considerations, were discussed during these sessions.
3. Ground Floors with Activity: A significant design flaw in the existing estate was the poorly lit areas adjacent to the garages that dominated the ground floor of the blocks — a common design feature in residential architecture of the time. Residents involved in the process pointed out the importance of increasing the sense of security when moving around these areas. A street-based design that activates the ground floor by enabling a greater variety of activities was central to the strategy. Alongside a clearer street layout and improved block entrances, bike racks, bin storage, and opportunities for non-residential and community uses were proposed to benefit both residents and the wider community. By repurposing areas previously used mainly for car parking into active spaces and by enhancing frontages with residential, commercial or community spaces, clear thresholds and boundaries are created to promote permeability and smooth transitions. Community facilities and local businesses are strategically located at corners and key activity nodes, facilitating passive surveillance and overlooking the public realm. The choice of materials also contributes to opening up the ground level; glazed lobbies and entrances connect indoor communal areas with adjacent outdoor spaces visually. Similarly, secondary entrances to existing blocks will be used to balance their function and prevent the creation of hidden or less frequented areas. Improved public lighting, new signage and a control system complement these strategies.
4. Broadwater Character & Scale: The architectural style known as Brutalism played a significant role in popularising the 'problem estate' narrative in Britain. This style was embraced by many of the country's modernist architects, leading to its prevalence in the social housing built during that period. Characterised by the predominant use of concrete, this style was celebrated by critic and advocate Reyner Banham for its memorable image, a clear exhibition of structure and honest expression of the material (Boughton, 2018). The monumentality and stark aesthetics of Brutalism provided an ideal setting for experimentation in the vast estates that were built during the latter half of the 20th century. These characteristics are evident in the design of Broadwater Farm.
Broadwater’s design framework acknowledges the latent potential of the existing architecture while addressing issues of materiality, building height, the links and spatial relationships between the infilled and redeveloped areas and the connection between the estate and its surroundings. The boundaries of the estate were revised to address the issue of it being perceived as an isolated entity, which was a common problem with many modernist estates. This was due to the fact that they were often of a particular size and density, which set them apart from their neighbours. In order to create a seamless transition with the surroundings, clear entrances to the estate are proposed, new materials are used that better match those of the vicinity, and a massing strategy is employed to avoid abrupt transitions in building heights.
The character of the estate was approached in a manner reminiscent of Kevin Lynch’s (1964) five elements of the city —paths, edges, districts, nodes and landmarks—, with particular emphasis on their importance in establishing a sense of place and enhancing the legibility of the urban environment. The proposal has engaged in a meticulous study of the local context, re-signifying existing elements such as the Kenley Tower, which has been retained as the tallest mass in the ensemble, in order to maintain its landmark character.
5. Good Quality Homes: The new blocks, arranged in courtyards that reflect the existing pattern of the estate, will replace the Tangmere and Northolt blocks. They will occupy a privileged position at the heart of the estate and offer an opportunity to transform the overall look of the scheme. These new blocks, complemented by infill development on nearby sites, will result in the creation of 294 new residential units, representing a net increase of 85 homes. The new dwellings, comprising three and four-bedroom family homes, will be managed by the council and rented out at social rates. A significant proportion of residents who participated in the public consultation highlighted the necessity for larger and more spacious accommodation, particularly for large families. In response to these demands, the design of the new flats incorporates larger and more flexible spaces as a key feature. Those who previously resided in the demolished blocks will be given priority for the new homes.
Furthermore, the introduction of new parks, public spaces, workspaces and a new well-being hub, which will house a doctor's surgery and other services, will help create a more active and dynamic ground floor, with activities that enhance the sense of place and welcome pedestrians. The architects have conducted an analysis of potential infill solutions to activate the ground floor, including the addition of one-bedroom flats that fit into the structural grid of the existing blocks. This in turn addresses the need to create a community that includes people of all ages and family types.
Management & Maintenance
The UDF exemplifies how regeneration projects can address current needs while allowing for future adaptations. This people-centred project fosters a sense of ownership through participation, which is crucial for the sustainability of the intervention. Stewardship is key, especially for the new collective spaces being created. Instead of a deterministic design approach, the framework considers what types of spaces can enhance the overall quality of life. It integrates social, economic, and environmental aspects that define the living and working experience in the area. These considerations are captured in the “Strategy for a Sustainable Neighbourhood.”
The bank of projects is a repository of proposed interventions within the project, illustrating the considerable interest in the long-term effects of the regeneration project and the substantial potential for future development. This section of the framework underscores the necessity for the formulation of a phased, structured and comprehensive planning and delivery strategy that allows for flexibility and input from existing and future residents. Consequently, management and maintenance are regarded as integral aspects of the design, alongside other tangible elements of the built environment.
With an approach strongly focused on creating social value and reducing the disruptive effects of regeneration. The architects have worked with the community to develop a masterplan that emphasises the use of existing assets, minimises demolition and establishes a hierarchy of priorities to maximise the positive impact in the long term.
L.Ricaurte. ESR15
Read more
->

York's Duncombe Square Housing: Towards Affordability, Sustainability, and Healthier Living
Created on 15-11-2024
Strengthening Construction Quality and Knowledge Sharing
The City of York's procurement strategy for the Duncombe Square project, as well as other housing sites across the city, focused on two key objectives: ensuring high-quality construction and facilitating knowledge exchange about sustainable building practices. These objectives exemplify the council's commitment to its housing delivery programme.
To achieve housing quality, the council engaged a multidisciplinary design team led by the esteemed architect Mikhail Riches, known for his work on Norwich Goldsmith Street and association with the Passivhaus Trust. This team was supported by RICS-accredited project managers, clerks of work, and valuers to uphold stringent standards.
The project used two complementary approaches to improve the construction and delivery of large-scale Passivhaus projects in the UK. The first approach involved training to advance sustainable construction skills for existing staff, new hires, and students aged 14 to 19, led by the main contractor, Caddick Construction (Passivhaus Trust, 2022). The second approach is sharing knowledge with a broader audience by organising multiple tours during the different construction phases. These tours were designed for developers, architects, researchers, and housing professionals. They showcased Duncombe Square as an open case study, allowing industry peers to learn from and engage directly with project and site managers, reinforcing the project's role as a model for York’s Housing Delivery Programme.
Duncombe Square Housing Design
The design principles of the Duncombe Square project aim to integrate functionality and encourage healthy and sustainable lifestyles. The principles embody the essence of Passivhaus design while ensuring aesthetic appeal. It features low-rise, high-density terraced housing to optimise land use and foster a sense of community. The terraces are strategically positioned close together to maximise solar gain during the winter hours of sunlight, ensuring compliance with the rigorous Passivhaus standards while accommodating a maximum number of residences. The design ensures that each home benefits from natural light and heat while aligning with the Passivhaus energy efficiency and ventilation principles.
The facade design and colour scheme connect with the local architectural identity of traditional Victorian terraces, with a modern twist that cares for indoor environmental quality. It features high ceilings, thick insulated walls, and a fully airtight construction. The design incorporates traditional materials such as brick, enhanced by modern touches of render and timber shingles that blend harmoniously with the local surroundings.
The site plan design reflects a neighbourhood concept that extends beyond the energy-efficient and modern appearance of the houses. Duncombe is designed as a child-friendly neighbourhood, prioritising walking and cycling with dedicated cycle parking for each home. Vehicle parking and circulation are situated along the site's perimeter, ensuring paths are exclusively for pedestrians and play areas. Additionally, shared 'ginnels' provide bike access, enhancing mobility and creating safe play areas for children. This emphasis on pedestrian access enhances community interaction and outdoor activities. The thoughtful landscaping incorporates generous green open spaces at the development's core, complemented by communal growing beds and private planters. These features are intended to be aesthetically pleasing while also encouraging community engagement.
A Construction Adventure
For the main contractor, Caddick Construction, this project represents a distinctive adventure - from procurement to construction to Passivhaus standards - that deviates from traditional British construction practices. Recent UK housing developments often employ "Design and Build" contracts, where the contractor assumes primary responsibility for designing and constructing the project. However, the architects led the design process in this case, necessitating frequent collaborative meetings to discuss detailed execution plans.
During a site visit to the project site in York in September 2023, the contractor’s site manager explained the challenges of constructing and applying Passivhaus standards on a large scale. Unlike traditional construction, Passivhaus demands meticulous attention to detail to ensure robust airtightness of the building envelope. Moreover, building to these standards involves sending progress images to a Passivhaus certifier, who verifies that each construction step meets the rigorous criteria before approving further progress.
The chosen construction method for this project is off-site timber frame construction combined with brick and roughcast render. Prefabricated timber frames mitigate risks for contractors and expedite the construction process. The homes' superstructure employs timber frame technology, ensuring durability and longevity.
A key priority in the construction process is preventing heat loss and moisture infiltration. This involves:
Envelope Insulation: Airtightness is crucial for minimising heat loss. Therefore, the façade installation included airtight boards, tapes, membranes, timber frame insulation, and triple-glazed windows. Indoor airtightness is tested at least four times throughout the construction process to guarantee that residents will live in an airtight house.
Foundation and Floor Insulation: Three layers of insulation between the floor finishing and foundation prevent heat loss, enhance thermal efficiency, and control moisture penetration, protecting against groundwater leakage.
Households’ Health and Wellbeing
Households' health and wellbeing are foundational pillars in the development of the Duncombe Square project. In addition to the robust energy efficiency benefits of Passivhaus standards, this initiative underscores high indoor air quality through Mechanical Ventilation with Heat Recovery (MVHR) units, which improve air quality and help mitigate issues like dampness and mould in airtight houses. To improve outdoor air quality, the design strategically reduces car usage by fostering a pedestrian-friendly environment with expansive green pathways that purify air and encourage outdoor activities. Amenities such as bike sheds with electric charging points and communal "cargo bikes" are also included.
Central to the project is a vibrant communal green space that facilitates relaxation, play, and social interactions—vital for mental and physical health. The scheme enhances residents' wellbeing by ensuring proximity to local amenities, promoting a healthier, more active lifestyle without reliance on vehicles. Extensive pedestrian and cycling paths, alongside wheelchair-friendly features, highlight the project's commitment to inclusivity and a healthy living environment. The design harmoniously integrates with local architecture and includes public amenity spaces that prioritise safe, child-friendly areas and places for social gatherings, fostering a strong community spirit.
When compared with the framework for sustainable housing focusing on health and wellbeing developed by Prochorskaite et al., (2016), the Duncombe project excels in incorporating features such as energy efficiency, thermal comfort, indoor air quality, noise prevention, daylight availability, and moisture control. Moreover, it emphasises accessible, quality public green spaces, attractive external views, and facilities encouraging social interaction and environmentally sustainable behaviours. Its compact neighbourhood design, sustainable transportation solutions, proximity to amenities, consideration of environmentally friendly construction materials, and efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions perfectly encapsulate the framework's objectives for providing sustainable housing focused on health and wellbeing.
Affordability
From a housing provider's perspective, the delivery team faced challenges in achieving a net-zero and Passivhaus standard that is affordable and scalable for large housing developments. For instance, construction costs are subject to pricing risks as contractors raise their prices amid market uncertainties, thereby increasing overall project expenses. Integrating Passivhaus principles is believed to have helped control these costs by simplifying building forms and reducing unnecessary complexities.
Residents' housing affordability is expected to be positively influenced by three key factors: tenure distribution, adherence to Passivhaus standards, and the development's central location. The tenure distribution includes 20% of units for social rent and 40% for shared ownership, offering affordable options for both renters and prospective homeowners. Passivhaus standards further reduce costs by lowering energy consumption through features like PV panels and energy-efficient air-source heat pumps, earning the development an A rating for energy performance and cutting utility bills for residents. Additionally, the central location decreases mobility-related expenses, with easy access to local amenities reducing the need for car use. Together, these factors help promote a sustainable lifestyle and lower overall living costs for residents.
Sustainability: Environmental, Social, and Economic Lens
Environmental sustainability involves two key aspects: (1) reducing resource consumption and (2) minimising emissions during use (Andersen et al., 2020). Duncombe Square's initiatives to reduce resource consumption include:
The dwelling's superstructure utilises low-carbon materials, such as FSC (Forest Steward Council) certified timber framing, which ensures it is sourced from sustainable forestry.
Using recycled newspaper for insulation to minimise environmental impact.
Monitoring the embodied energy of construction materials, including accounting for the energy used in their extraction, production, and transportation.
Sourcing 70% of subcontractors and supplies within 30 miles of the site, as per Passivhaus Trust guidelines, to reduce emissions from long-distance transportation.
To minimise environmental impact during use, the project incorporates:
Air-source heat pumps for heating and solar PV panels on roofs, enabling net-zero carbon energy usage.
Water butts for collecting rainwater for gardening purposes.
Permeable surfaces, rain gardens, and Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDS) to reduce surface runoff in public areas.
Economic sustainability is at the forefront of providing affordable, energy-efficient dwellings that do not impose long-term financial burdens on residents. The project offers affordable dwellings in terms of housing costs, non-housing costs, and housing quality. It also contributes to the broader economy by promoting sustainable building practices and creating future jobs through on-site training programmes. Caddick Construction prioritises the local sourcing of subcontractors and suppliers within 30 miles of the site, thereby reducing transportation costs and supporting the local economy.
Social sustainability is integral to the project, featuring designs that promote community interaction and provide safe, accessible outdoor spaces. The development includes communal green spaces, such as plant-growing areas and a central green space for natural play, enhancing residents' quality of life. Prioritising pedestrian pathways and extensive cycle storage encourages a shift towards sustainable transport options, reducing reliance on cars and promoting healthier, more active lifestyles.
A.Elghandour. ESR4
Read more
->